@metamask/react-native-payments
v2.0.2
> This project is currently in __beta and APIs are subject to change.__
0/weekUpdated 2 months agoMITUnpacked: 131.1 KB
Published by Naoufal Kadhom
npm install @metamask/react-native-payments> This project is currently in __beta and APIs are subject to change.__
React Native Payments




Accept Payments with Apple Pay and Android Pay using the Payment Request API.
__Features__
- __Simple.__ No more checkout forms.
- __Effective__. Faster checkouts that increase conversion.
- __Future-proof__. Use a W3C Standards API, supported by companies like Google, Firefox and others.
- __Cross-platform__. Share payments code between your iOS, Android, and web apps.
- __Add-ons__. Easily enable support for Stripe or Braintree via add-ons.
---
Table of Contents
- Demo
- Installation
- Usage
- Testing Payments
- Apple Pay button
- Add-ons
- API
- Resources
- License
Demo
You can run the demo by cloning the project and running:
``shell`
$ yarn run:demo
In a rush? Check out the browser version of the demo.
_Note that you'll need to run it from a browser with Payment Request support._
Installation
First, download the package:
`
shell
$ yarn add react-native-payments
`
Second, link the native dependencies:
shell
$ react-native link react-native-payments
`Usage
- Setting up Apple Pay/Android Pay
- Importing the Library
- Initializing the Payment Request
- Displaying the Payment Request
- Aborting the Payment Request
- Requesting Contact Information
- Requesting a Shipping Address
- Processing Payments
- Dismissing the Payment Request
$3
Before you can start accepting payments in your App, you'll need to setup Apple Pay and/or Android Pay.#### Apple Pay
1. Register as an Apple Developer
1. Obtain a merchant ID
1. Enable Apple Pay in your app
Apple has a documentation on how to do this in their _Configuring your Environment_ guide.
#### Android Pay
1. Add Android Pay and Google Play Services to your dependencies
1. Enable Android Pay in your Manifest
Google has documentation on how to do this in their _Setup Android Pay_ guide.
$3
Once Apple Pay/Android Pay is enabled in your app, jump into your app's entrypoint and make the globally available to your app.`es6
// index.ios.js
global.PaymentRequest = require('react-native-payments').PaymentRequest;
`$3
To initialize a Payment Request, you'll need to provide and PaymentDetails.#### Payment Method Data
The Payment Method Data is where you defined the forms of payment that you accept. To enable Apple Pay, we'll define a
supportedMethod of apple-pay. We're also required to pass a data object to configures Apple Pay. This is where we provide our merchant id, define the supported card types and the currency we'll be operating in.`es6
const METHOD_DATA = [{
supportedMethods: ['apple-pay'],
data: {
merchantIdentifier: 'merchant.com.your-app.namespace',
supportedNetworks: ['visa', 'mastercard', 'amex'],
countryCode: 'US',
currencyCode: 'USD'
}
}];
`
See Android Pay Example
es6
const METHOD_DATA = [{
supportedMethods: ['android-pay'],
data: {
supportedNetworks: ['visa', 'mastercard', 'amex'],
currencyCode: 'USD',
environment: 'TEST', // defaults to production
paymentMethodTokenizationParameters: {
tokenizationType: 'NETWORK_TOKEN',
parameters: {
publicKey: 'your-pubic-key'
}
}
}
}];
`#### Payment Details
Payment Details is where define transaction details like display items, a total and optionally shipping options.
Google has excellent documentation for Defining Payment Details.
es6
const DETAILS = {
id: 'basic-example',
displayItems: [
{
label: 'Movie Ticket',
amount: { currency: 'USD', value: '15.00' }
}
],
total: {
label: 'Merchant Name',
amount: { currency: 'USD', value: '15.00' }
}
};
`Once you've defined your
and details, you're ready to initialize your Payment Request.`es6
const paymentRequest = new PaymentRequest(METHOD_DATA, DETAILS);
`🚨 _Note: On Android, display items are not displayed within the Android Pay view. Instead, the _User Flows documentation_ suggests showing users a confirmation view where you list the display items. When using React Native Payments, show this view after receiving the
._$3
Now that you've setup your Payment Request, displaying it is as simple as calling the show method.`es6
paymentRequest.show();
`
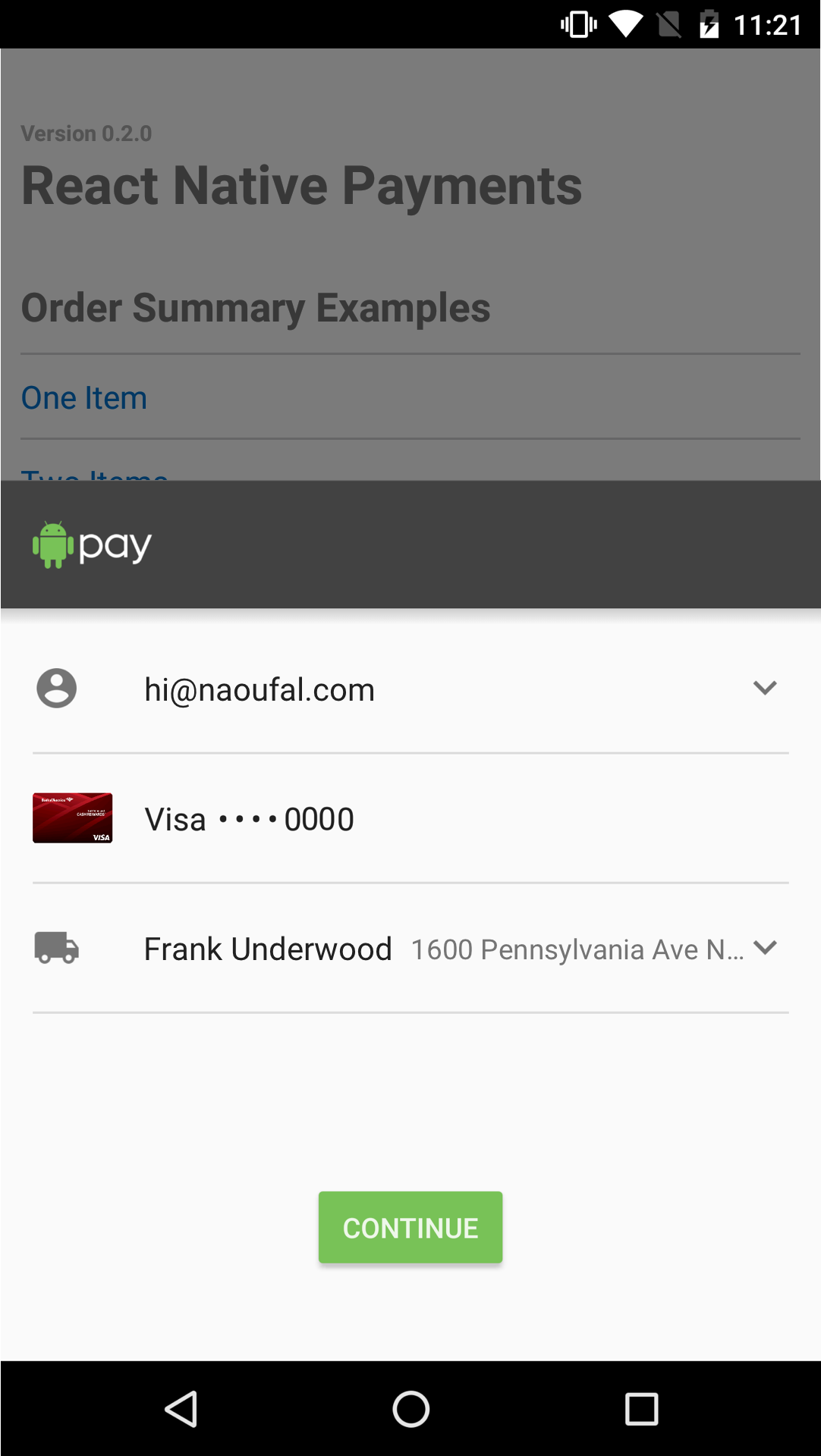
See Screenshots
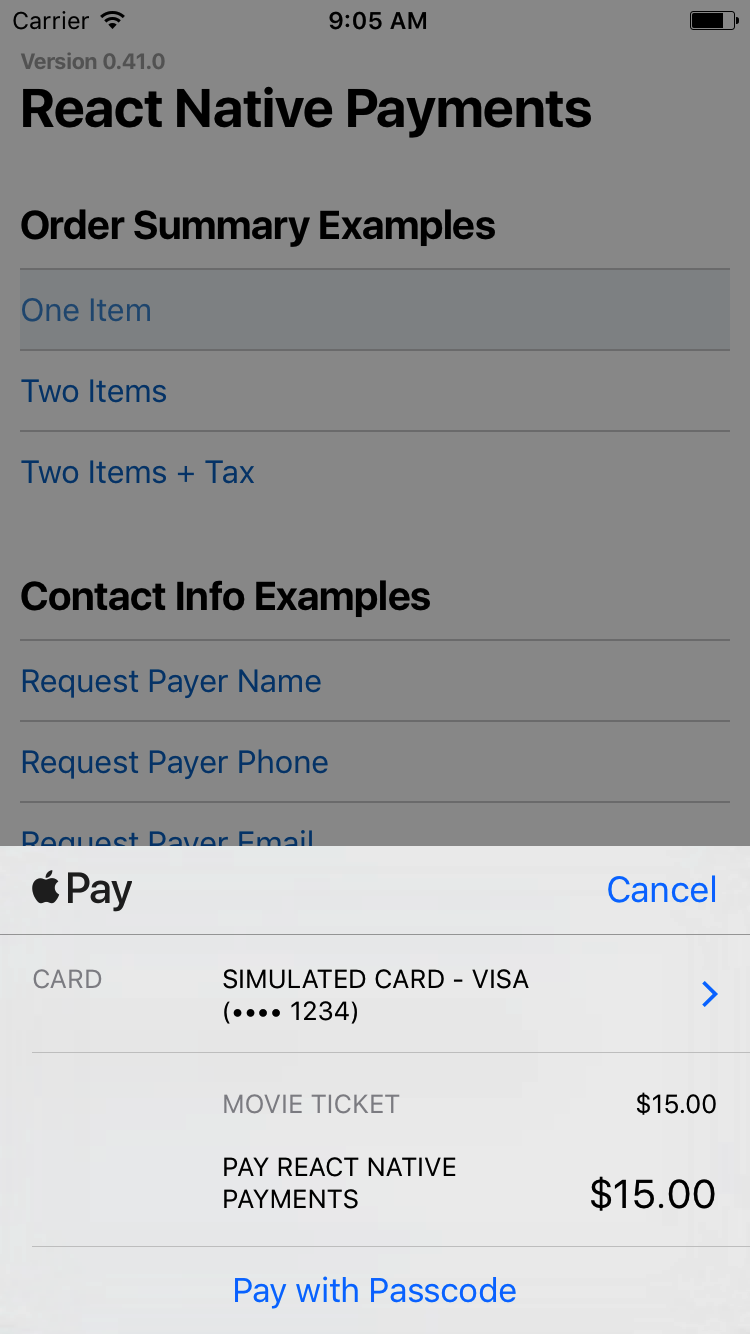
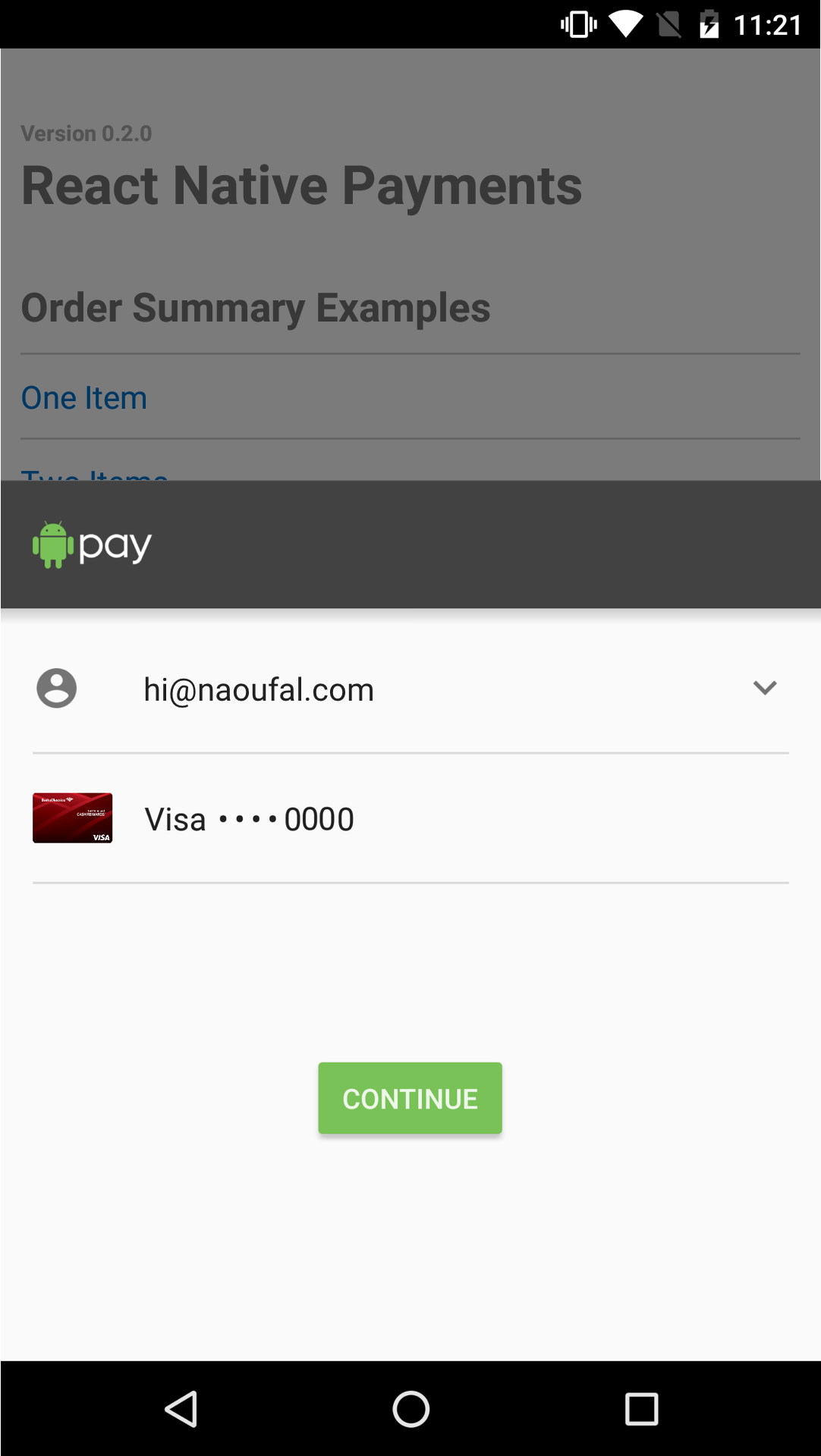
$3
You can abort the Payment Request at any point by calling the method.`es6
paymentRequest.abort();
`🚨 _Note: Not yet implemented on Android Pay_
$3
Some apps may require contact information from a user. You can do so by providing a []() as a third argument when initializing a Payment Request. Using Payment Options, you can request a contact name, phone number and/or email.#### Requesting a Contact Name
Set
requestPayerName to true to request a contact name.`es6
const OPTIONS = {
requestPayerName: true
};
`
See Screenshots
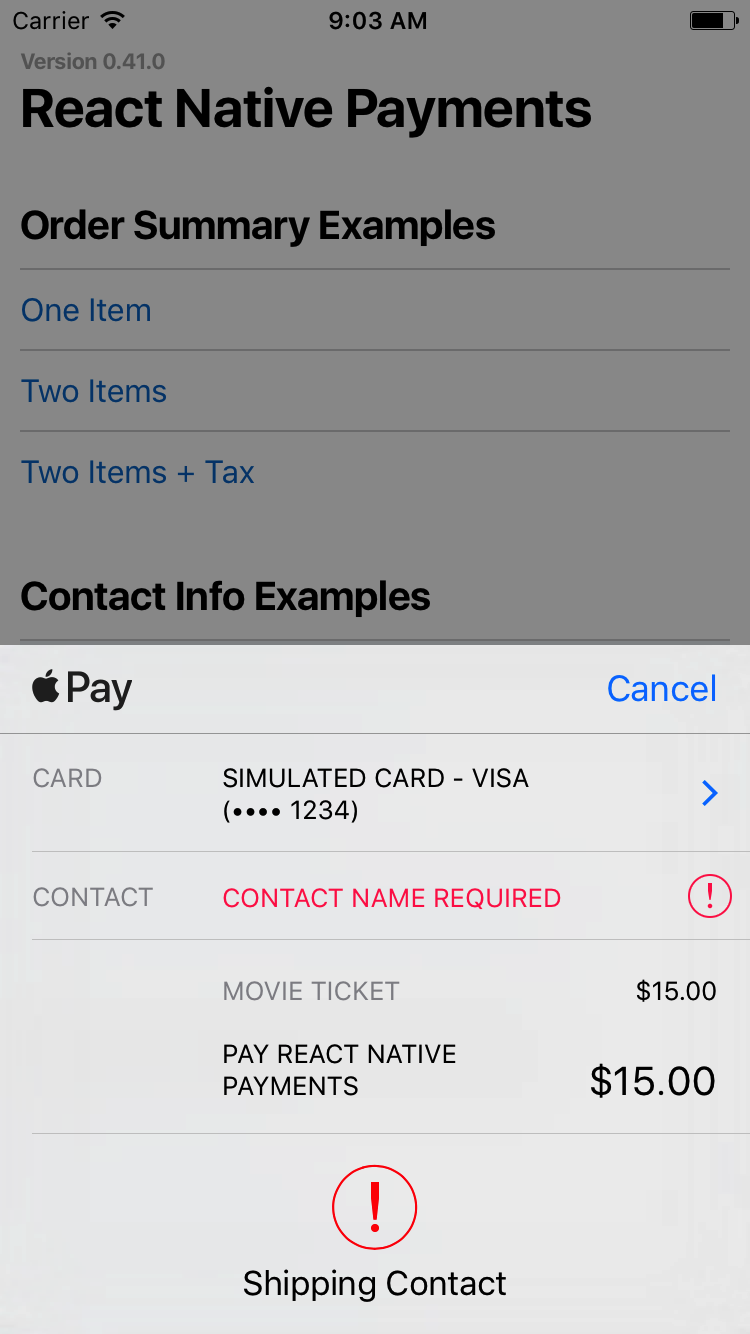

🚨 _Note: On Android, requesting a contact name will present the user with a shipping address selector. If you're not shipping anything to the user, consider capturing the contact name outside of Android Pay._
#### Requesting a Phone Number
Set
to true to request a phone number.`es6
const OPTIONS = {
requestPayerPhone: true
};
`
See Screenshots
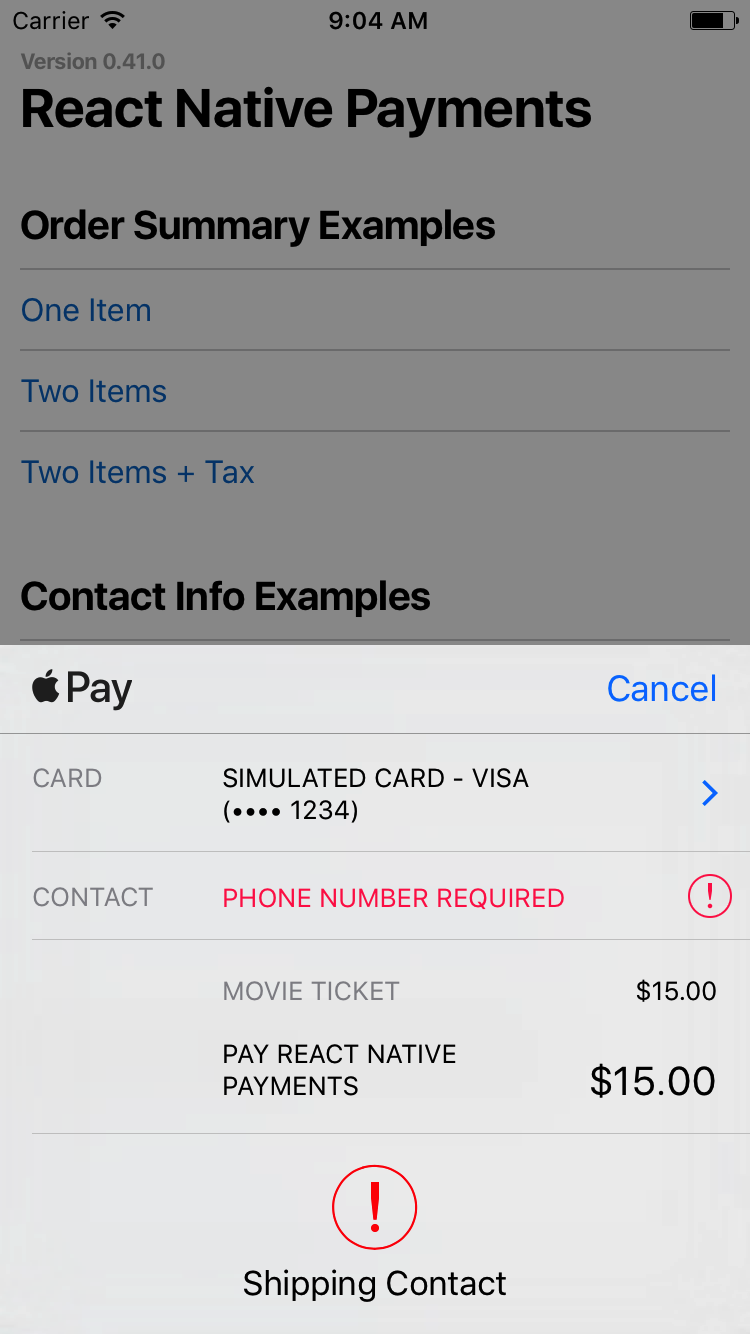

🚨 _Note: On Android, requesting a phone number will present the user with a shipping address selector. If you're not shipping anything to the user, consider capturing the phone number outside of Android Pay._
#### Requesting an Email Address
Set
to true to request an email address.`es6
const OPTIONS = {
requestPayerEmail: true
};
`
See Screenshots
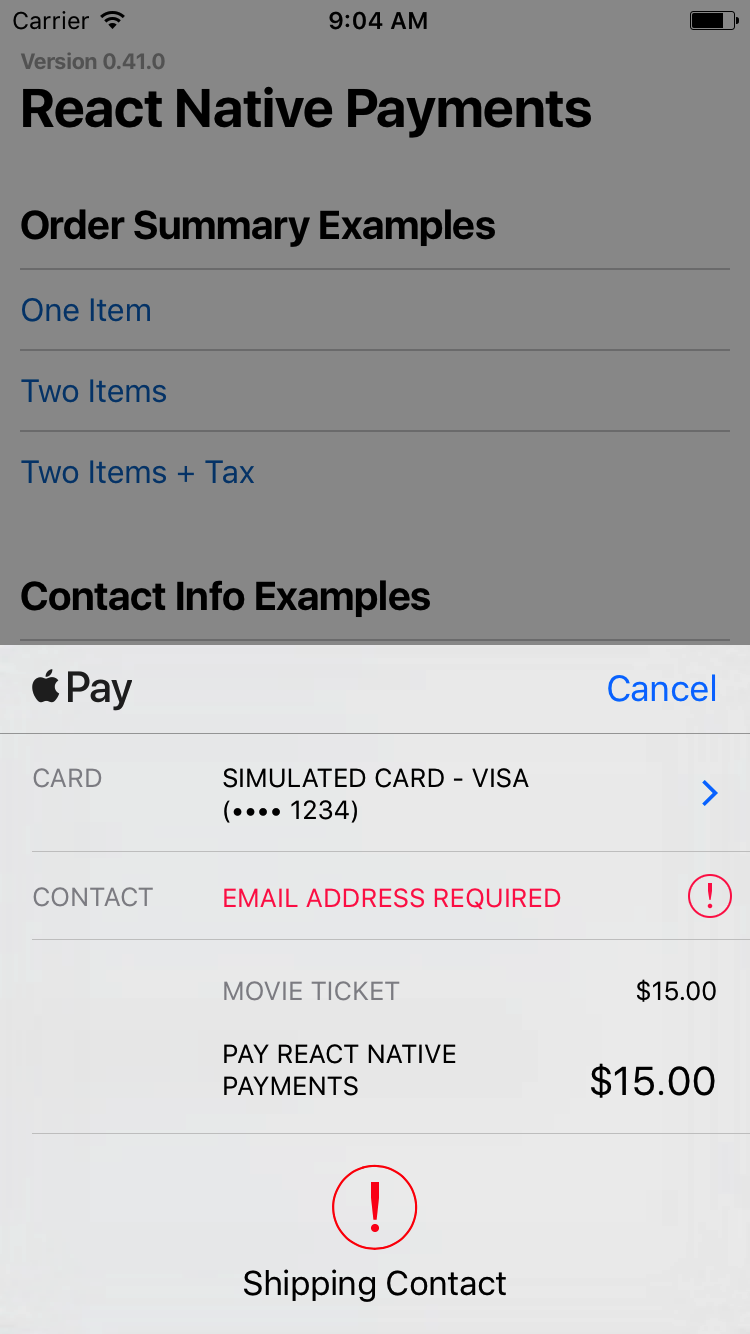

You can also request all three by setting them all to
.`es6
const OPTIONS = {
requestPayerName: true,
requestPayerPhone: true,
requestPayerEmail: true
};
`$3
Requesting a shipping address is done in three steps.First, you'll need to set
to true within PaymentOptions.`es6
const OPTIONS = {
requestShipping: true
};
`Second, you'll need to include
in your Payment Details.`diff
const DETAILS = {
id: 'basic-example',
displayItems: [
{
label: 'Movie Ticket',
amount: { currency: 'USD', value: '15.00' }
}
],
+ shippingOptions: [{
+ id: 'economy',
+ label: 'Economy Shipping',
+ amount: { currency: 'USD', value: '0.00' },
+ detail: 'Arrives in 3-5 days' // detail is specific to React Native Payments
+ }],
total: {
label: 'Merchant Name',
amount: { currency: 'USD', value: '15.00' }
}
};
`Lastly, you'll need to register event listeners for when a user selects a
and/or a shippingOption. In the callback each event, you'll need to provide new PaymentDetails that will update your PaymentRequest.`es6
paymentRequest.addEventListener('shippingaddresschange', e => {
const updatedDetails = getUpdatedDetailsForShippingAddress(paymentRequest.shippingAddress; e.updateWith(updatedDetails);
});
paymentRequest.addEventListener('shippingoptionchange', e => {
const updatedDetails = getUpdatedDetailsForShippingOption(paymentRequest.shippingOption);
e.updateWith(updatedDetails);
});
`For a deeper dive on handling shipping in Payment Request, checkout Google's _Shipping in Payment Request_.
🚨 _Note: On Android, there are no
and shippingoptionchange events. To allow users to update their shipping address, you'll need to trigger a new PaymentRequest. Updating shipping options typically happens after the receiving the PaymentResponse and before calling its getPaymentToken method._$3
Now that we know how to initialize, display, and dismiss a Payment Request, let's take a look at how to process payments.When a user accepts to pay,
PaymentRequest.show will resolve to a Payment Response.`es6
paymentRequest.show()
.then(paymentResponse => {
// Your payment processing code goes here return processPayment(paymentResponse);
});
`There are two ways to process Apple Pay/Android Pay payments -- on your server or using a payment processor.
#### Processing Payments on Your Server
If you're equipped to process Apple Pay/Android Pay payments on your server, all you have to do is send the Payment Response data to your server.
> ⚠️ Note: When running Apple Pay on simulator,
equals to null.`es6
import { NativeModules } from 'react-native';paymentRequest.show()
.then(paymentResponse => {
const { transactionIdentifier, paymentData } = paymentResponse.details;
return fetch('...', {
method: 'POST',
body: {
transactionIdentifier,
paymentData
}
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(successHandler)
.catch(errorHandler)
});
`
See Android Pay Example
es6
paymentRequest.show()
.then(paymentResponse => {
const { getPaymentToken } = paymentResponse.details; return getPaymentToken()
.then(paymentToken => {
const { ephemeralPublicKey, encryptedMessage, tag } = paymentResponse.details;
return fetch('...', {
method: 'POST',
body: {
ephemeralPublicKey,
encryptedMessage,
tag
}
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(successHandler)
.catch(errorHandler)
});
});
`
You can learn more about server-side decrypting of Payment Tokens on Apple's Payment Token Format Reference documentation.
#### Processing Payments with a Payment Processor
When using a payment processor, you'll receive a
field within the details of the PaymentResponse. Use this token to charge customers with your payment processor.`es6
paymentRequest.show()
.then(paymentResponse => {
const { paymentToken } = paymentResponse.details; // On Android, you need to invoke the getPaymentToken method to receive the paymentToken. return fetch('...', {
method: 'POST',
body: {
paymentToken
}
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(successHandler)
.catch(errorHandler);
});
`
See Android Pay Example
es6
paymentRequest.show()
.then(paymentResponse => {
const { getPaymentToken } = paymentResponse.details; return getPaymentToken()
.then(paymentToken => fetch('...', {
method: 'POST',
body: {
paymentToken
}
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(successHandler)
.catch(errorHandler);
});
});
`
For a list of supported payment processors and how to enable them, see the Add-ons section.
$3
Dismissing the Payment Request is as simple as calling the method on of the PaymentResponse.`es6
paymentResponse.complete('success'); // Alternatively, you can call it with fail or unknown
🚨 _Note: On Android, there is no need to call
Testing Payments
$3
The sandbox environment is a great way to test offline implementation of Apple Pay for apps, websites, and point of sale systems. Apple offers detailed guide for setting up sandbox environment.
> ⚠️ Note: It is also important to test Apple Pay in your production environment. Real cards must be used in the production environment. Test cards will not work.
>
> ⚠️ Note: There are known differences when running Apple Pay on simulator and real device. Make sure you test Apple Pay on real device before going into production.
Apple Pay Button
Provides a button that is used either to trigger payments through Apple Pay or to prompt the user to set up a card.
Detailed docs and examples
Add-ons
Here's a list of Payment Processors that you can enable via add-ons:
- Stripe
- Braintree
🚨 _Note: On Android, Payment Processors are enabled by default._
API
$3
$3
$3
$3
Resources
$3
- Introducing the Payment Request API
- Deep Dive into the Payment Request API
- W3C API Working Draft
- Web Payments
- The Future of Web Payments
$3
- Getting Started with Apple Pay
- Configuring your Environment
- Processing Payments
- Payment Token Format Reference
$3
- Setup Android Pay
- Tutorial
- Brand Guidelines
- Gateway Token Approach
- Network Token Approach
License
Licensed under the MIT License, Copyright © 2017, Naoufal Kadhom.
See LICENSE for more information.