A Three.js and R3F implementation of Precomputed Atmospheric Scattering
npm install @takram/three-atmosphere 
A Three.js and R3F (React Three Fiber) implementation of Eric Bruneton's Precomputed Atmospheric Scattering.
This library is part of a project to prototype the rendering aspect of a Web GIS engine. For more details on the background and current status of this project, please refer to the main README.
``sh`
npm install @takram/three-atmosphere
pnpm add @takram/three-atmosphere
yarn add @takram/three-atmosphere
Peer dependencies include three and postprocessing, as well as @react-three/fiber, @react-three/postprocessing, and @react-three/drei when using R3F.
`
three postprocessing
@react-three/fiber @react-three/postprocessing @react-three/drei
Suitable for large-scale scenes, but supports only Lambertian BRDF.
Lighting is applied in AerialPerspectiveEffect. Materials must be unlit (e.g. MeshBasicMaterial) and the render buffer is considered albedo.
`tsx
import { EffectComposer } from '@react-three/postprocessing'
import {
AerialPerspective,
Atmosphere,
Sky
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
const Scene = () => (
)
`
!Example of post-process lighting
→ Storybook
!Example of post-process lighting
→ Storybook
Compatible with built-in Three.js materials and shadows, but both direct and indirect irradiance are approximated only for small-scale scenes.
Objects are lit by SunDirectionalLight, SkyLightProbe, and possibly other light sources.
`tsx
import { EffectComposer } from '@react-three/postprocessing'
import {
AerialPerspective,
Atmosphere,
Sky,
SkyLight,
SunLight
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
const Scene = () => (
)
`
!Example of light-source lighting
→ Storybook
Selectively applies the post-process and light-source lighting using LightingMaskPass or an MRT texture. It combines the advantages of both, but transparency over the post-process lighting is not supported.
`tsx
import { EffectComposer } from '@react-three/postprocessing'
import {
AerialPerspective,
Atmosphere,
LightingMask,
Sky,
SkyLight,
SunLight
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { Layers } from 'three'
const LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER = 10
const layers = new Layers()
layers.enable(LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER)
const Scene = () => (
{/ This mesh is lit in post-process. /}
{/ This mesh is lit by light sources. /}
)
`
!Example of mixed lighting
→ Storybook
`tsx
import { useFrame } from '@react-three/fiber'
import {
Atmosphere,
Sky,
type AtmosphereApi
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { useRef } from 'react'
const Scene = () => {
const atmosphereRef = useRef
useFrame(() => {
atmosphereRef.current?.updateByDate(new Date())
})
return (
...
)
}
`
See the story for complete example.
`ts
const position = new Vector3(/ ECEF coordinate in meters /)
// SkyMaterial disables projection. Provide a plane that covers clip space.
const skyMaterial = new SkyMaterial()
const sky = new Mesh(new PlaneGeometry(2, 2), skyMaterial)
sky.frustumCulled = false
sky.position.copy(position)
scene.add(sky)
// SkyLightProbe computes sky irradiance of its position.
const skyLight = new SkyLightProbe()
skyLight.position.copy(position)
scene.add(skyLight)
// SunDirectionalLight computes sunlight transmittance to its target position.
const sunLight = new SunDirectionalLight()
sunLight.target.position.copy(position)
scene.add(sunLight)
scene.add(sunLight.target)
// Demonstrates light-source lighting here. For post-process lighting, set
// sunLight and skyLight to true, remove SkyLightProbe and
// SunDirectionalLight, and provide a normal buffer to AerialPerspectiveEffect.
const aerialPerspective = new AerialPerspectiveEffect(camera)
// Use floating-point render buffer, as radiance/luminance is stored here.
const composer = new EffectComposer(renderer, {
frameBufferType: HalfFloatType
})
composer.addPass(new RenderPass(scene, camera))
composer.addPass(
new EffectPass(
camera,
aerialPerspective,
new ToneMappingEffect({ mode: ToneMappingMode.AGX })
)
)
const generator = new PrecomputedTexturesGenerator(renderer)
generator.update().catch((error: unknown) => {
console.error(error)
})
const { textures } = generator
Object.assign(skyMaterial, textures)
sunLight.transmittanceTexture = textures.transmittanceTexture
skyLight.irradianceTexture = textures.irradianceTexture
Object.assign(aerialPerspective, textures)
const sunDirection = new Vector3()
const moonDirection = new Vector3()
function render(): void {
// Suppose date is updated elsewhere.
getSunDirectionECEF(date, sunDirection)
getMoonDirectionECEF(date, moonDirection)
skyMaterial.sunDirection.copy(sunDirection)
skyMaterial.moonDirection.copy(moonDirection)
sunLight.sunDirection.copy(sunDirection)
skyLight.sunDirection.copy(sunDirection)
aerialPerspective.sunDirection.copy(sunDirection)
sunLight.update()
skyLight.update()
composer.render()
}
`
- The reference frame is fixed to ECEF and cannot be configured, #11.
- The aerial perspective (specifically the inscatter term) includes a workaround for the horizon artifact, but due to finite floating-point precision, this artifact cannot be removed completely.
- Volumetric light shaft is not implemented as it requires ray tracing or an additional depth pass from the sun. You may notice scattered light is not occluded by scene objects.
- Although you can generate custom precomputed textures, the implementation is effectively limited to Earth's atmosphere. For rendering atmospheres of other planets, consider implementing Sébastien Hillaire's A Scalable and Production Ready Sky and Atmosphere Rendering Technique.
- Currently developed using GLSL. It does not use node-based TSL yet, and WebGPU is not supported, but both are planned.
I have observed some confusion between the _post-process lighting_ and _light-source lighting_. This is a follow-up note.
The _post-process lighting_ represents the correct lighting model, except that the current implementation only supports the Lambertian BRDF. Surfaces are lit in the post-processing stage by AerialPerspectiveEffect when sunLight and skyLight are enabled. It could support various BRDFs if we could afford deferred rendering, but not quite yet, especially without TSL.
Pixel values in the render buffer (the output of RenderPass) are considered _surface albedo_ and are usually rendered using MeshBasicMaterial. MeshBasicMaterial is an unlit material and is not affected by light sources in the scene.
The _light-source lighting_ approximates the post-process lighting by taking the incoming radiance computed at a single point in the scene using SunDirectionalLight and SkyLightProbe and applying it to every point in the scene.
It offers other BRDFs using built-in materials such as MeshPhysicalMaterial. Such materials are lit materials, and their outgoing radiance (lit by light sources) is stored in the render buffer (completely black if there are no light sources), so they cannot be considered surface albedo.
Fortunately, since MeshBasicMaterial is always unlit regardless of light sources, we can store both albedo and lit surface radiance information in a single render buffer. This will produce the correct results if we enable sunLight and skyLight only for albedo pixels. That's the purpose of LightingMaskPass.
Rules of thumb:
- Use MeshBasicMaterial under _post-process lighting_.sunLight
- Any materials can be used under _light-source lighting_.
- Don't enable or skyLight on AerialPerspectiveEffect when using SunDirectionalLight and SkyLightProbe, unless correctly masked using LightingMaskPass.
The underlying concepts of these components and classes might be a bit complex. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the Issues or Discussions.
Interfaces
R3F components
- Atmosphere
- Sky
- Stars
- SkyLight
- SunLight
- AerialPerspective
- LightingMask
Three.js
- AtmosphereMaterialBase
- SkyMaterial
- StarsMaterial
- SkyLightProbe
- SunDirectionalLight
- AerialPerspectiveEffect
- LightingMaskPass
- PrecomputedTexturesGenerator
- PrecomputedTexturesLoader
Functions
- getSunDirectionECEF
- getMoonDirectionECEF
- getECIToECEFRotationMatrix
- getSunLightColor
An interface for the collection of precomputed textures.
`ts`
interface PrecomputedTextures {
irradianceTexture: Texture
scatteringTexture: Data3DTexture
transmittanceTexture: Texture
singleMieScatteringTexture?: Data3DTexture
higherOrderScatteringTexture?: Data3DTexture
}
#### transmittanceTexture
A 2D LUT texture that contains the transmittance between an arbitrary point in the atmosphere and the atmosphere's top boundary. The LUT is parameterized by view height and the angle between view direction and zenith.
#### scatteringTexture
A 4D LUT packed into a 3D texture. It contains the Rayleigh scattering and the red component of single Mie scattering terms. The LUT is parameterized by view height, the angle between view direction and zenith, the angle between sun direction and zenith, and the angle between view and sun direction.
#### irradianceTexture
A 2D LUT texture that contains the indirect irradiance on horizontal surfaces. The LUT is parameterized by view height and the angle between sun direction and zenith.
#### singleMieScatteringTexture
An optional LUT texture that contains the full RGB components of the single Mie scattering term. This might reduce artifacts when the red component of the single Mie scattering term is very small.
This texture is not required until you encounter problems.
#### higherOrderScatteringTexture
An optional LUT texture that contains only higher-order (N ≥ 2) scattering terms. By using this information, it can attenuate only single scattering in the shadowed segments of rays.
This texture is not required unless you have shadow length information, or you use the clouds package with the lightShafts option enabled.
Provides and synchronizes props of atmosphere components. It's the recommended way to configure components unless you need finer control over properties of individual components.
→ Source
`tsx
import { useFrame, useLoader, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import {
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL,
PrecomputedTexturesLoader
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import {
Atmosphere,
Sky,
type AtmosphereApi
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { useRef } from 'react'
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader()
const Scene = () => {
const atmosphereRef = useRef
useFrame(() => {
// Computes sun direction, moon direction and ECI to ECEF rotation
// matrix by the date, then propagates them to descendant components via
// context.
atmosphereRef.current?.updateByDate(new Date())
})
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const textures = useLoader(
loader.setType(renderer),
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL
)
return (
...
)
}
`
#### textures
`ts`
textures: PrecomputedTextures | string = undefined
The precomputed textures, or a URL to the directory containing them.
If left undefined, the textures will be generated using PrecomputedTexturesGenerator.
#### ellipsoid
`ts`
ellipsoid: Ellipsoid = Ellipsoid.WGS84
The ellipsoid model representing Earth.
#### correctAltitude
`ts`
correctAltitude: boolean = true
Whether to adjust the atmosphere's inner sphere to osculate (touch and share a tangent with) the ellipsoid.
The atmosphere is approximated as a sphere, with a radius between the ellipsoid's major and minor axes. The difference can exceed 10,000 meters in worst cases, roughly equal to the cruising altitude of a passenger jet. This option compensates for this difference.
An example at an altitude of 2,000 meters and a latitude of 35°:
| correctAltitude = false | correctAltitude = true |
| :-: | :-: |
|  |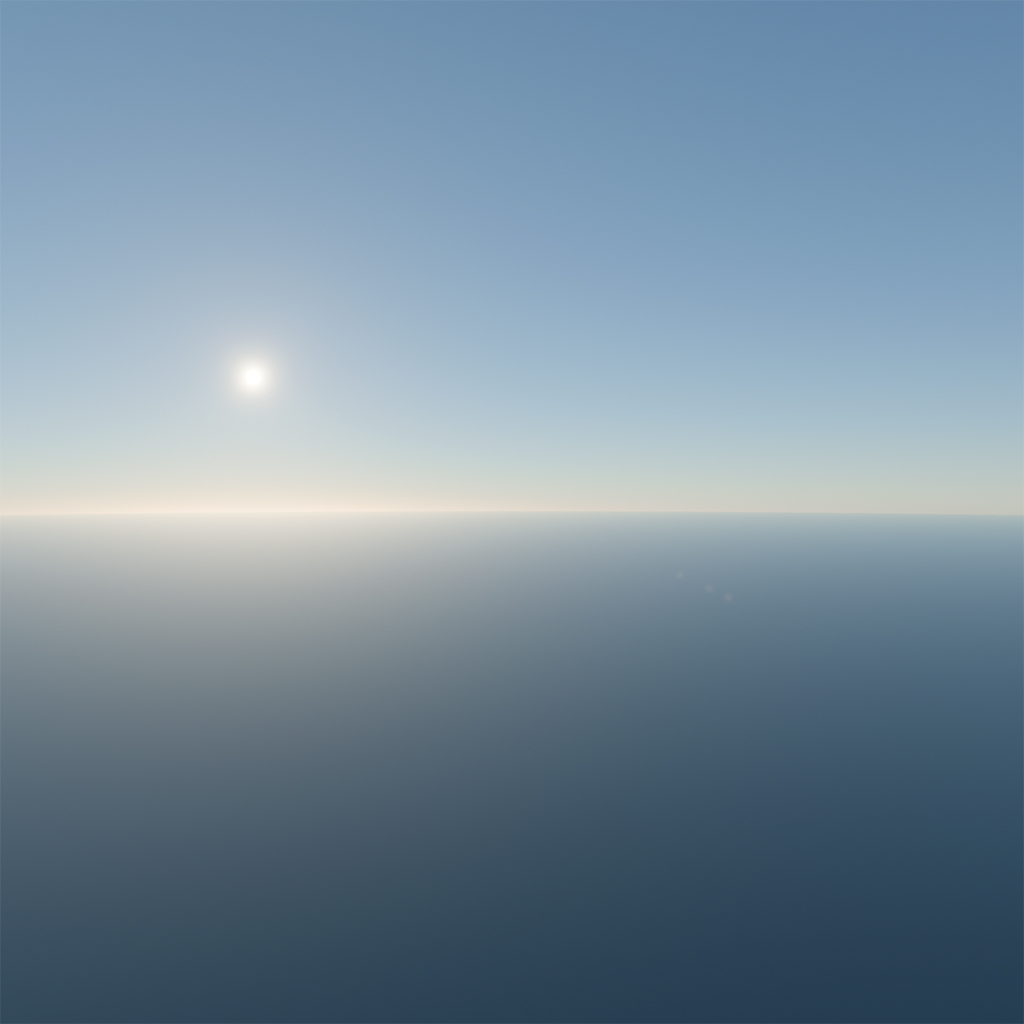  |
#### date
`ts`
date: number | Date = undefined
Specifies the date used to obtain the directions of the sun, moon, and ECI to ECEF rotation matrix.
The behavior when used together with the updateByDate function is not defined.
#### sunDirection, moonDirection
`ts`
sunDirection: Vector3
moonDirection: Vector3
The normalized direction to the sun and moon in ECEF coordinates. This value is shared with descendant components and is overwritten by the date prop or the updateByDate function.
The default values are [0, 0, 0].
#### inertialToECEFMatrix
`ts`
inertialToECEFMatrix: Matrix4
The rotation matrix for converting ECI to ECEF coordinates. This value is shared with descendant components and is overwritten by the date prop or the updateByDate function.
The default value is an identity matrix.
#### worldToECEFMatrix
`ts`
worldToECEFMatrix: Matrix4
The matrix for converting world coordinates to ECEF coordinates. Use this matrix to define a reference frame or, more commonly, to orient the ellipsoid for working near the world space origin and adapting to Three.js's Y-up coordinate system.
The default value is an identity matrix, and it must be orthogonal and consist only of translation and rotation (no scaling).
`ts
import { type AtmosphereApi } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { Ellipsoid } from '@takram/three-geospatial'
import { Vector3 } from 'three'
const position = new Vector3(/ ECEF coordinate in meters /)
const east = new Vector3()
const north = new Vector3()
const up = new Vector3()
declare const atmosphere: AtmosphereApi
// Move and rotate the ellipsoid so that the world space origin locates at
// the given geographic coordinate, and the scene's orientation aligns with
// X: north, Y: up, Z: east, for example.
Ellipsoid.WGS84.getEastNorthUpVectors(position, east, north, up)
atmosphere.worldToECEFMatrix.makeBasis(north, up, east).setPosition(position)
// Alternatively in this case, simply:
Ellipsoid.WGS84.getNorthUpEastFrame(position, atmosphere.worldToECEFMatrix)
`
See the story for complete example.
#### updateByDate
`ts`
function updateByDate(date: number | Date): void
Updates the directions of the sun, moon, and the ECI to ECEF rotation matrix for the specified date. Use this function via the ref instead of the date prop if you want to update it smoothly.
The behavior when used together with the date prop is not defined.
Displays the sky in a screen quad.
See SkyMaterial for further details.
→ Source
`tsx
import { useLoader } from '@react-three/fiber'
import {
getMoonDirectionECEF,
getSunDirectionECEF
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { Sky } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
const sunDirection = getSunDirectionECEF(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const moonDirection = getMoonDirectionECEF(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const Scene = () => (
)
`
The parameters of AtmosphereMaterialBase and SkyMaterial are exposed as props.
Represents the brightest stars as points at an infinite distance.
See StarsMaterial for further details.
→ Source
`tsx
import { useLoader } from '@react-three/fiber'
import {
getECIToECEFRotationMatrix,
getSunDirectionECEF
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { Stars } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { ArrayBufferLoader } from '@takram/three-geospatial'
const sunDirection = getSunDirectionECEF(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const inertialToECEFMatrix =
getECIToECEFRotationMatrix(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const Scene = () => {
const starsData = useLoader(ArrayBufferLoader, '/assets/stars.bin')
return (
sunDirection={sunDirection}
matrix={inertialToECEFMatrix}
/>
)
}
`
The parameters of AtmosphereMaterialBase and StarsMaterial are also exposed as props.
#### data
`ts`
data: ArrayBuffer | string = DEFAULT_STARS_DATA_URL
The data containing the position and magnitude of the stars, or a URL to it.
If left undefined, the data will be loaded directly from GitHub.
A light probe for indirect sky irradiance.
See SkyLightProbe for further details.
→ Source
`tsx
import { useLoader, useLoader, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import {
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL,
getSunDirectionECEF,
PrecomputedTexturesLoader
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { SkyLight } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { DataTexture, Vector3 } from 'three'
const position = new Vector3(/ ECEF coordinate in meters /)
const sunDirection = getSunDirectionECEF(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader()
const Scene = () => {
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const { irradianceTexture } = useLoader(
loader.setType(renderer),
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL
)
return (
position={position}
sunDirection={sunDirection}
/>
)
}
`
The parameters of SkyLightProbe are exposed as props.
A directional light representing the sun.
See SunDirectionalLight for further details.
→ Source
`tsx
import { useLoader, useLoader, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import {
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL,
getSunDirectionECEF,
PrecomputedTexturesLoader
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { SunLight } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { DataTexture, Vector3 } from 'three'
const position = new Vector3(/ ECEF coordinate in meters /)
const sunDirection = getSunDirectionECEF(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader()
const Scene = () => {
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const { transmittanceTexture } = useLoader(
loader.setType(renderer),
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL
)
return (
position={position}
sunDirection={sunDirection}
/>
)
}
`
The parameters of SunDirectionalLight are exposed as props.
A post-processing effect that renders atmospheric transparency and inscattered light.
See AerialPerspectiveEffect for further details.
→ Source
`tsx
import { useLoader, useLoader, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { EffectComposer } from '@react-three/postprocessing'
import {
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL,
getSunDirectionECEF,
PrecomputedTexturesLoader
} from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { AerialPerspective } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { Vector3 } from 'three'
const sunDirection = getSunDirectionECEF(/ Date object or timestamp /)
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader()
const Scene = () => {
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const textures = useLoader(
loader.setType(renderer),
DEFAULT_PRECOMPUTED_TEXTURES_URL
)
return (
)
}
`
The parameters of AerialPerspectiveEffect are exposed as props.
A post-processing pass that renders a mask for the mixed lighting.
See LightingMaskPass for further details.
→ Source
`tsx
import { EffectComposer } from '@react-three/postprocessing'
import { Atmosphere, LightingMask } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
import { Layers } from 'three'
const LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER = 10
const layers = new Layers()
layers.enable(LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER)
const Scene = () => {
return (
{/ This mesh is included in the mask. /}
{/ This mesh is masked out. /}
)
}
`
The parameters of LightingMaskPass are exposed as props.
The base class of SkyMaterial and StarsMaterial.
→ Source
#### irradianceTexture, scatteringTexture, transmittanceTexture, singleMieScatteringTexture, higherOrderScatteringTexture
`ts`
irradianceTexture: Texture | null = null
scatteringTexture: Data3DTexture | null = null
transmittanceTexture: Texture | null = null
singleMieScatteringTexture: Data3DTexture | null = null
higherOrderScatteringTexture: Data3DTexture | null = null
The precomputed textures.
#### ellipsoid
`ts`
ellipsoid: Ellipsoid = Ellipsoid.WGS84
See ellipsoid.
#### worldToECEFMatrix
`ts`
worldToECEFMatrix: Matrix4
See worldToECEFMatrix.
#### correctAltitude
`ts`
correctAltitude: boolean = true
See correctAltitude.
#### sunDirection
`ts`
sunDirection: Vector3 = new Vector3()
The normalized direction to the sun in ECEF coordinates.
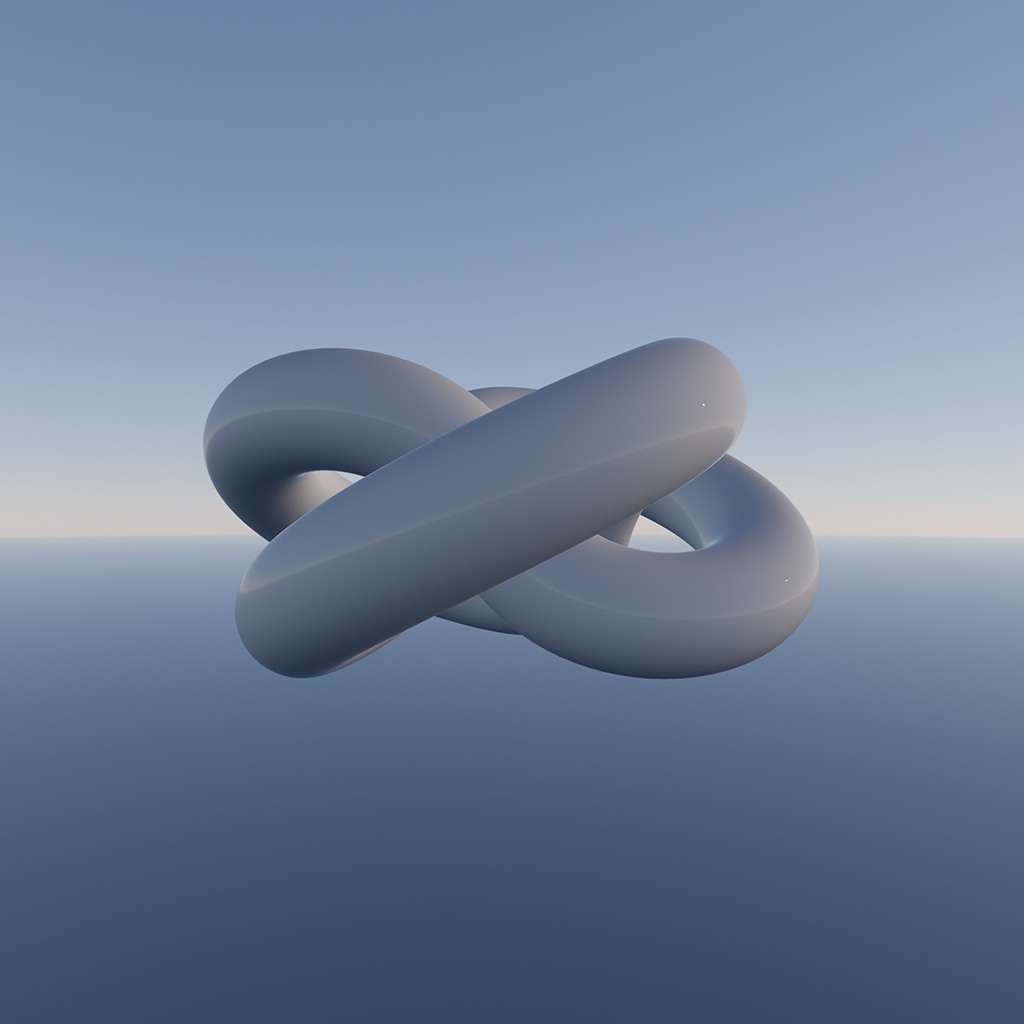
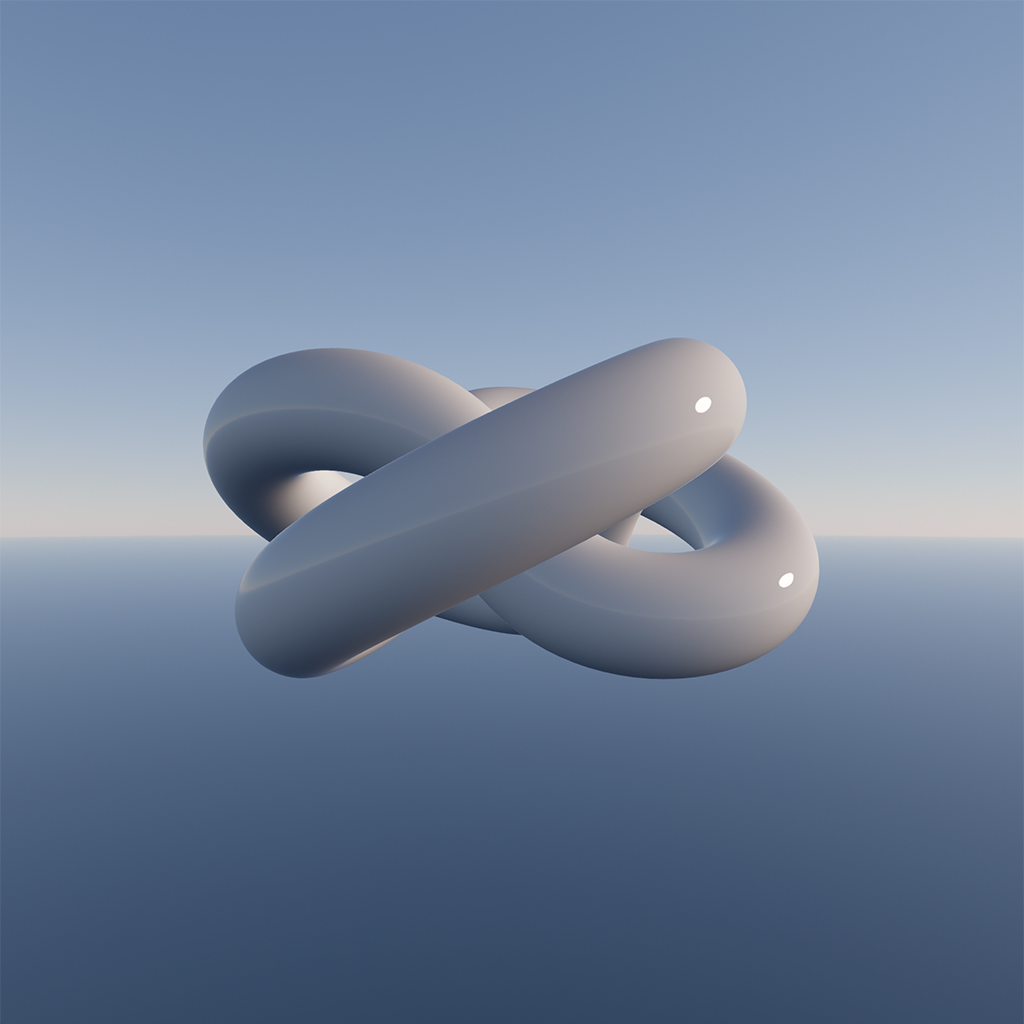
#### sunAngularRadius
`ts`
sunAngularRadius: number = 0.004675
The angular radius of the sun, in radians.
Increase this value if the sun flickers in a low-resolution environment map. Modifying this value does not affect the sky's total radiance unless the sun is partially visible.
| sunAngularRadius = 0.004675 | sunAngularRadius = 0.1 |
| :-: | :-: |
|  |  |
A material for displaying the sky. Apply this to a screen quad.
Despite its name, this material renders the atmosphere itself, along with the sun and moon. When viewed from within the atmosphere, it appears as the sky. From space, it represents Earth's atmosphere with a flat ground.
→ Source
`ts`
const material = new SkyMaterial()
getSunDirectionECEF(date, material.sunDirection)
const sky = new Mesh(new PlaneGeometry(2, 2), material)
sky.frustumCulled = false
scene.add(sky)
Extends AtmosphereMaterialBase.
#### sun, moon
`ts`
sun: boolean = true
moon: boolean = true
Whether to display the sun and moon.
#### moonDirection
`ts`
moonDirection: Vector3 = new Vector()
The normalized direction to the moon in ECEF coordinates.
#### moonAngularRadius
`ts`
moonAngularRadius: number = 0.0045
The angular radius of the moon, in radians.
#### lunarRadianceScale
`ts`
lunarRadianceScale: number = 1
A scaling factor to adjust the brightness of the moon.
| lunarRadianceScale = 1 | lunarRadianceScale = 5 |
| :-: | :-: |
|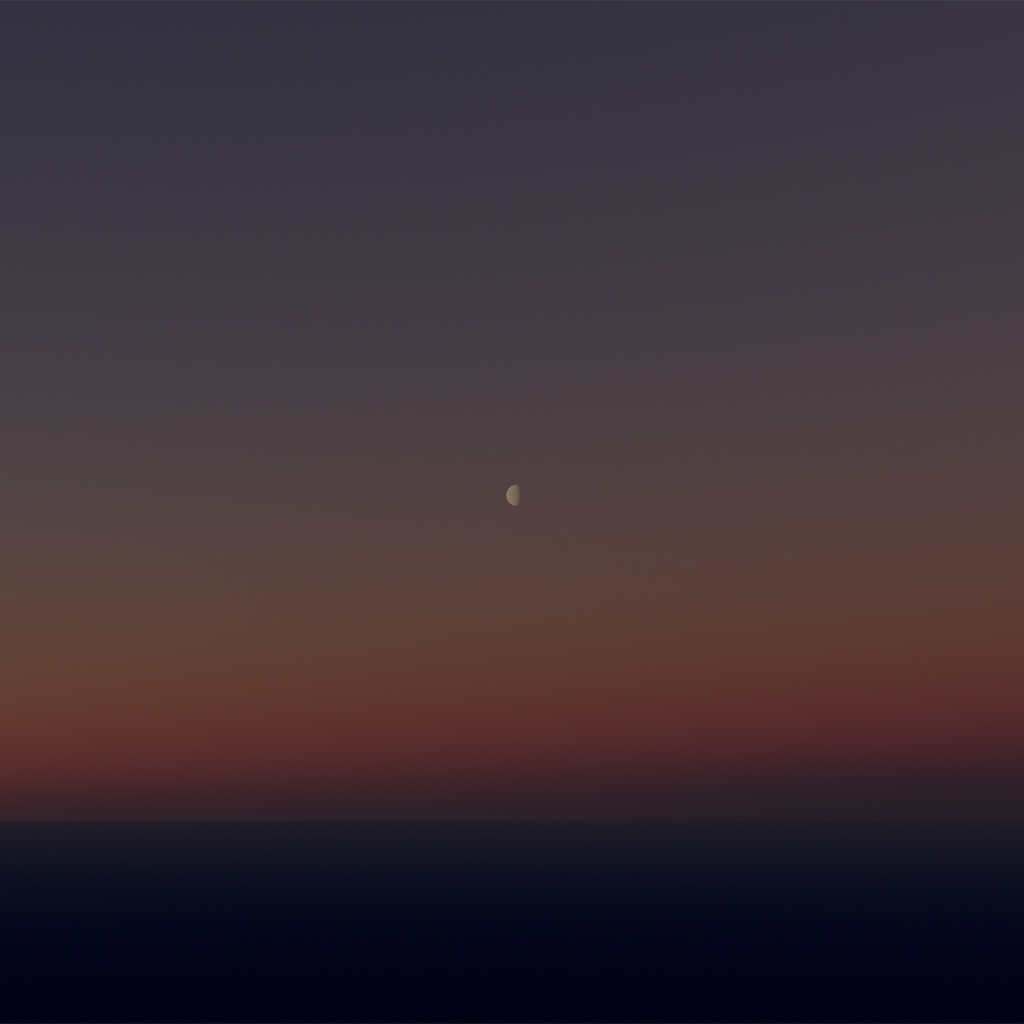  |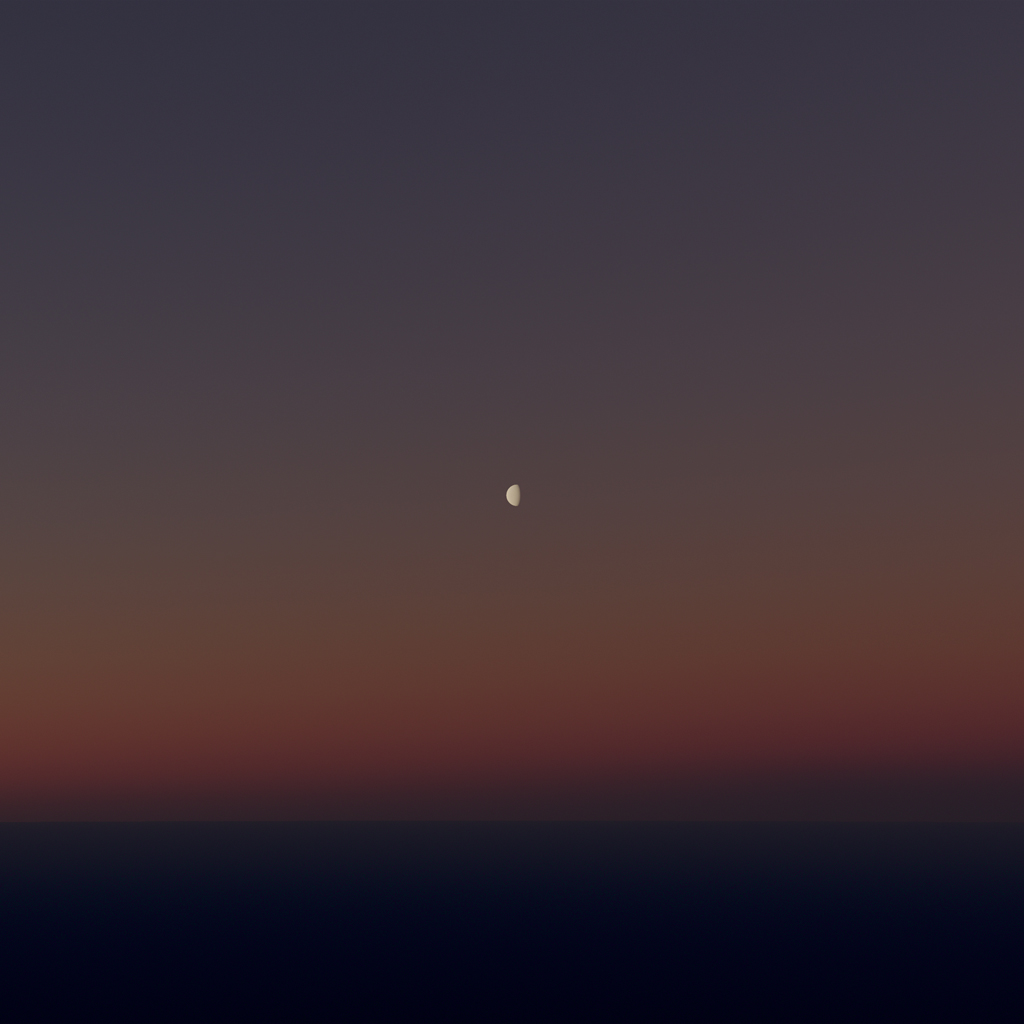  |
#### groundAlbedo
`ts`
groundAlbedo: Color = new Color()
The albedo of the ground. Defaults to 0.
Represents the brightest stars as points at an infinite distance.
The provided data (stars.bin) contains the J2000 ECI directions, magnitudes and black body chromaticities of the 9,096 stars listed in Yale Bright Star Catalog version 5.
→ Source
`ts`
const material = new StarsMaterial({
irradianceTexture,
scatteringTexture,
transmittanceTexture
})
getSunDirectionECEF(date, material.sunDirection)
const stars = new Points(
new StarsGeometry(await new ArrayBufferLoader(url).loadAsync()),
material
)
stars.setRotationFromMatrix(getECIToECEFRotationMatrix(date))
scene.add(stars)
Extends AtmosphereMaterialBase.
#### pointSize
`ts`
pointSize: number = 1
The size of each star, in points.
#### intensity
`ts`
intensity: number = 1
A scaling factor to adjust the brightness of the stars.
#### background
`ts`
background: boolean = true
Whether to display the stars at an infinite distance, otherwise, they appear on a unit sphere.
A light probe for indirect sky irradiance.
It calculates spherical harmonics of sky irradiance at its position by sampling the precomputed irradiance texture on the CPU.
→ Source
`ts
const skyLight = new SkyLightProbe({ irradianceTexture })
skyLight.position.set(position)
getSunDirectionECEF(date, skyLight.sunDirection)
scene.add(skyLight)
skyLight.update()
`
Extends LightProbe
#### irradianceTexture
`ts`
irradianceTexture: Texture | null = null
The precomputed irradiance texture.
#### ellipsoid
`ts`
ellipsoid: Ellipsoid = Ellipsoid.WGS84
See ellipsoid.
#### worldToECEFMatrix
`ts`
worldToECEFMatrix: Matrix4
See worldToECEFMatrix.
#### correctAltitude
`ts`
correctAltitude: boolean = true
See correctAltitude
#### sunDirection
`ts`
sunDirection: Vector3 = new Vector3()
See sunDirection.
A directional light representing the sun.
It calculates the sun's radiance by sampling the precomputed transmittance texture on the CPU.
→ Source
`ts
const sunLight = new SunDirectionalLight({ transmittanceTexture })
sunLight.target.position.set(position)
getSunDirectionECEF(date, sunLight.sunDirection)
scene.add(sunLight)
scene.add(sunLight.target)
sunLight.update()
`
Extends DirectionalLight
#### transmittanceTexture
`ts`
transmittanceTexture: Texture | null = null
The precomputed transmittance texture.
#### ellipsoid
`ts`
ellipsoid: Ellipsoid = Ellipsoid.WGS84
See ellipsoid.
#### worldToECEFMatrix
`ts`
worldToECEFMatrix: Matrix4
See worldToECEFMatrix.
#### correctAltitude
`ts`
correctAltitude: boolean = true
See correctAltitude
#### sunDirection
`ts`
sunDirection: Vector3 = new Vector3()
See sunDirection.
Note it's the direction to the sun, not that of light.
#### distance
`ts`
distance: number = 1
The distance from the target. Adjust this value if shadows are enabled for the light, as it may need to cover the entire scene.
A post-processing effect that renders atmospheric transparency and inscattered light. It can optionally render sun and sky irradiance as post-process lighting.
This is for use with the postprocessing's EffectComposer and is not compatible with the one in Three.js examples.
→ Source
`ts
const aerialPerspective = new AerialPerspectiveEffect(camera, {
irradianceTexture,
scatteringTexture,
transmittanceTexture,
higherOrderScatteringTexture
})
getSunDirectionECEF(position, aerialPerspective.sunDirection)
const composer = new EffectComposer(renderer, {
frameBufferType: HalfFloatType
})
composer.addPass(new RenderPass(scene, camera))
composer.addPass(
new EffectPass(
camera,
aerialPerspective,
new ToneMappingEffect({ mode: ToneMappingMode.AGX })
)
)
`
Extends postprocessing's Effect.
#### normalBuffer
`ts`
normalBuffer: Texture | null = null
The normal buffer used for post-process lighting. It is not required if both sunLight and skyLight are disabled.
EffectComposer's default normal buffer lacks sufficient precision, causing banding in shaded areas. Using a floating-point normal buffer resolves this issue.
#### octEncodedNormal
`ts`
octEncodedNormal: boolean = false
Indicates that the normal is oct-encoded and stored in the first two elements of the normal buffer texels.
#### reconstructNormal
`ts`
reconstructNormal: boolean = false
Whether to reconstruct normals from depth buffer.
#### irradianceTexture, scatteringTexture, transmittanceTexture, singleMieScatteringTexture, higherOrderScatteringTexture
`ts`
irradianceTexture: Texture | null = null
scatteringTexture: Data3DTexture | null = null
transmittanceTexture: Texture | null = null
singleMieScatteringTexture: Data3DTexture | null = null
higherOrderScatteringTexture: Data3DTexture | null = null
The precomputed textures.
#### ellipsoid
`ts`
ellipsoid: Ellipsoid = Ellipsoid.WGS84
See ellipsoid.
#### worldToECEFMatrix
`ts`
worldToECEFMatrix: Matrix4
See worldToECEFMatrix.
#### correctAltitude
`ts`
correctAltitude: boolean = true
See correctAltitude
#### correctGeometricError
`ts`
correctGeometricError: boolean = true
This option corrects lighting artifacts caused by geometric errors in surface tiles. The Earth's surface normals are gradually morphed to a true sphere.
Disable this option if your scene contains objects that penetrate the atmosphere or are located in space.
| correctGeometricError = false | correctGeometricError = true |
| :-: | :-: |
| 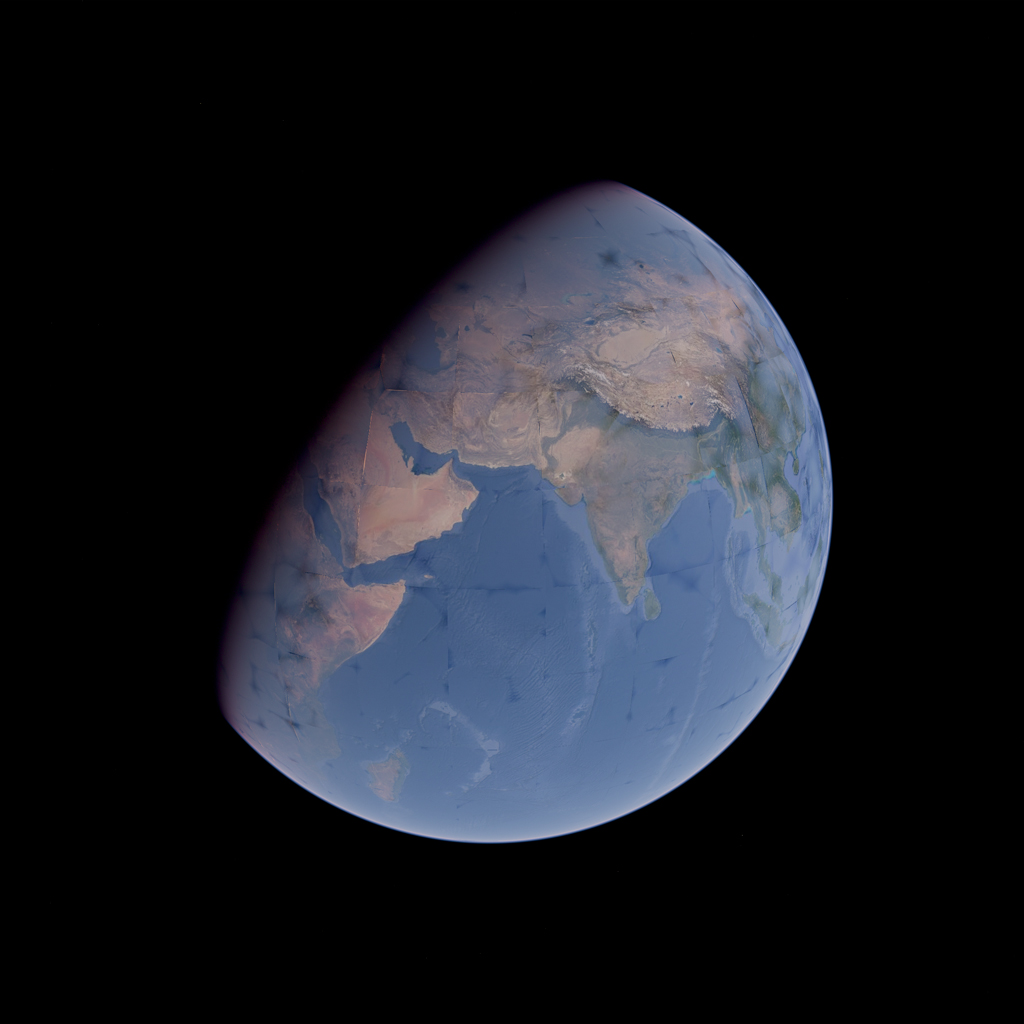 | 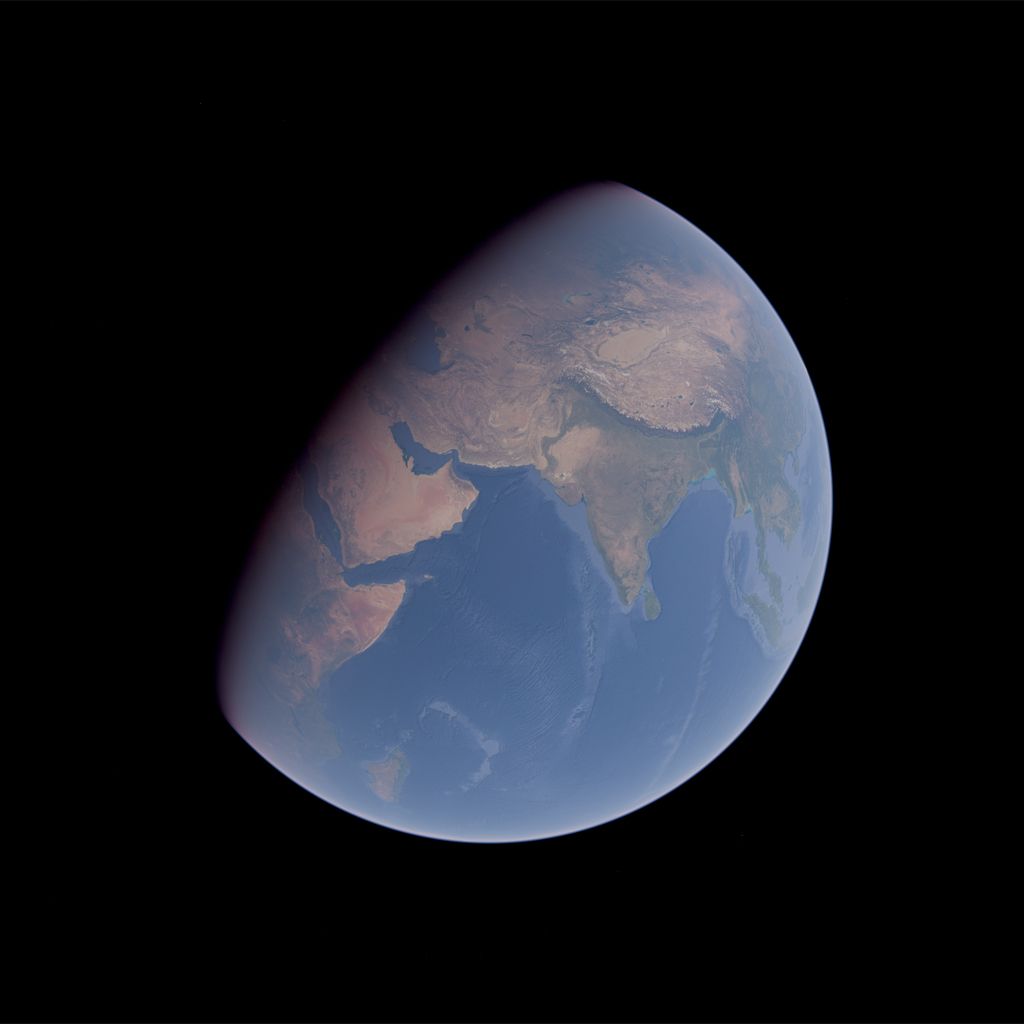 |
#### sunDirection
`ts`
sunDirection: Vector3 = new Vector3()
See sunDirection.
#### sunLight, skyLight
`ts`
sunLight: boolean = false
skyLight: boolean = false
Whether to apply sun and sky irradiance as post-process lighting.
Enabling one without the other is physically incorrect and should only be done for debugging.
#### transmittance, inscatter
`ts`
transmittance: boolean = true
inscatter: boolean = true
Whether to account for the atmospheric transmittance and inscattered light.
#### albedoScale
`ts`
albedoScale: number = 1
This value adjusts the color buffer to reduce contrast.
Post-process lighting treats the color buffer as albedo, but textures like those in Google Photorealistic 3D Tiles have baked lighting and shadows, resulting in higher contrast. Adjusting this value helps make it less noticeable.
#### sky
`ts`
sky: boolean = false
Whether to render the sky as a post-processing effect. Enabling this may reduce the total number of fragments needed to compute the sky radiance.
In this case, the Sky component is redundant and should be omitted.
#### sun, moon
`ts`
sun: boolean = true
moon: boolean = true
See sun, moon.
#### moonDirection
`ts`
moonDirection: Vector3 = new Vector()
See moonDirection.
#### moonAngularRadius
`ts`
moonAngularRadius: number = 0.0045
See moonAngularRadius.
#### lunarRadianceScale
`ts`
lunarRadianceScale: number = 1
See lunarRadianceScale.
A post-processing pass that renders a mask for the mixed lighting.
If you can afford using MRT, it is preferable to render this mask in your render pass instead.
→ Source
`ts
const LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER = 10
const layers = new Layers()
layers.enable(LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER)
const lightingMask = new LightingMaskPass(scene, camera)
lightingMask.selectionLayers = LIGHTING_MASK_LAYER
const aerialPerspective = new AerialPerspectiveEffect(camera, {
irradianceTexture,
scatteringTexture,
transmittanceTexture
})
const composer = new EffectComposer(renderer, {
frameBufferType: HalfFloatType
})
composer.addPass(new RenderPass(scene, camera))
composer.addPass(lightingMask)
composer.addPass(
new EffectPass(
camera,
aerialPerspective,
new ToneMappingEffect({ mode: ToneMappingMode.AGX })
)
)
`
#### selectionLayer
`ts`
selectionLayer: number = / The next unique layer on creation /
Specifies the layer to which the meshes are assigned for rendering to the mask.
#### inverted
`ts`
inverted: boolean = false
By default, meshes with the selection layer are masked out from the post-process lighting. Set this to true when rendering the objects for the post-process lighting is less expensive (generally, fewer triangles) than that for the light-source lighting, and configure the layers accordingly.
A class for generating the precomputed textures.
→ Source
`ts
const generator = new PrecomputedTexturesGenerator(renderer, options)
generator.update().catch(error => {
console.error(error)
})
const aerialPerspective = new AerialPerspectiveEffect(camera, {
...generator.textures
})
`
#### type
`ts`
type: AnyFloatType = / Depends on the renderer's capabilities /
Specifies the type of intermediate render targets and precomputed textures. It defaults to FloatType if the provided renderer supports the linear filtering on FloatType. Otherwise, it falls back to HalfFloatType.
#### combinedScattering
`ts`
combinedScattering: boolean = true
Setting this option to false generates the singleMieScatteringTexture.
See singleMieScatteringTexture for further details.
#### higherOrderScattering
`ts`
higherOrderScattering: boolean = true
Specifies whether to generate the higherOrderScatteringTexture.
See higherOrderScatteringTexture for further details.
#### textures
`ts`
textures: PrecomputedTextures
The generated precomputed textures.
#### update
`ts`
async update(): Promise
Performs the precomputation and updates the textures property.
This is an async function that performs precomputation incrementally over multiple frames so that you can render a meaningful result earlier. It doesn't need to be awaited because the textures in the textures property are allocated when the instance is created.
#### dispose
`ts`
dispose(options?: { textures: boolean = true }): void
Frees the GPU-related resources allocated by this instance, as usual.
Setting the optional textures flag to false doesn't deallocate the precomputed textures, effectively transferring their ownership to the caller.
#### Suspend until textures are fully generated
`ts
import { Canvas, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { Suspense, useEffect } from 'react'
import { suspend } from 'suspend-react'
import { PrecomputedTexturesGenerator } from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { Atmosphere } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
const Scene = () => {
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const textures = suspend(async () => {
const generator = new PrecomputedTexturesGenerator(renderer)
const textures = await generator.update()
// Transfers ownership of the textures. We are now responsible for
// deallocating them when they are no longer needed.
generator.dispose({ textures: false })
return textures
}, [PrecomputedTexturesGenerator, renderer])
useEffect(() => {
return () => {
for (const texture of Object.values(textures)) {
texture?.dispose()
}
}
}, [textures])
return
}
const App = () => (
)
`
An aggregated loader class for the precomputed textures.
→ Source
`ts
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader(options).setType(renderer)
const textures = loader.load(url)
const aerialPerspective = new AerialPerspectiveEffect(camera, {
...textures
})
`
#### format
`ts`
format: 'exr' | 'binary' = 'exr'
Specifies the format of precomputed textures to load.
#### type
`ts`
type: AnyFloatType = HalfFloatType
Specifies the type of precomputed textures.
#### combinedScattering
`ts`
combinedScattering: boolean = true
Setting this option to false loads the singleMieScatteringTexture.
See singleMieScatteringTexture for further details.
#### higherOrderScattering
`ts`
higherOrderScattering: boolean = true
Specifies whether to load the higherOrderScatteringTexture.
See higherOrderScatteringTexture for further details.
#### setType
`ts`
setType(renderer: WebGLRenderer): this
Sets the type of precomputed textures to FloatType if the provided renderer supports the linear filtering on FloatType. Otherwise, it falls back to HalfFloatType.
#### Non-blocking texture loading
`ts
import { Canvas, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { useMemo } from 'react'
import { PrecomputedTexturesLoader } from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { Atmosphere } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader()
const Scene = () => {
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const textures = useMemo(
() => loader.setType(renderer).load(url),
[renderer]
)
return
}
const App = () => (
)
`
#### Suspend until textures are fully loaded
`ts
import { Canvas, useLoader, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { Suspense } from 'react'
import { PrecomputedTexturesLoader } from '@takram/three-atmosphere'
import { Atmosphere } from '@takram/three-atmosphere/r3f'
const loader = new PrecomputedTexturesLoader()
const Scene = () => {
const renderer = useThree(({ gl }) => gl)
const textures = useLoader(loader.setType(renderer), url)
return
}
const App = () => (
)
`
`ts`
function getSunDirectionECEF(date: number | Date, result?: Vector3): Vector3
function getMoonDirectionECEF(date: number | Date, result?: Vector3): Vector3
Obtains the direction to the sun and moon in ECEF coordinates for the specified UTC time. This internally uses astronomy-engine and it approximates UTC as being equivalent to UT1.
→ Source
`ts`
function getECIToECEFRotationMatrix(
date: number | Date,
result?: Matrix4
): Matrix4
Obtains the rotation matrix to convert coordinates from J2000 ECI to ECEF. This internally uses astronomy-engine and it approximates UTC as being equivalent to UT1.
→ Source
`ts
interface SunLightColorOptions {
ellipsoid?: Ellipsoid
correctAltitude?: boolean
}
function getSunLightColor(
transmittanceTexture: Texture,
worldPosition: Vector3,
sunDirection: Vector3,
result?: Color,
options?: SunLightColorOptions
): Color
``
Calculates the radiance of sunlight observed from a given position by sampling the precomputed transmittance texture on the CPU.
→ Source
In alphabetical order
- A Scalable and Production Ready Sky and Atmosphere Rendering Technique
- Outdoor Light Scattering Sample Update
- Physically Based Real-Time Rendering of Atmospheres using Mie Theory
- Precomputed Atmospheric Scattering
Implementation references
- Precomputed Atmospheric Scattering
- Yale Bright Star Catalog version 5