@thi.ng/rstream-graph
v4.1.210TypeScript
Declarative dataflow graph construction for @thi.ng/rstream
0/weekUpdated yesterdayApache-2.0Unpacked: 39.5 KB
Published by Karsten Schmidt
npm install @thi.ng/rstream-graph!@thi.ng/rstream-graph

!npm downloads

> [!NOTE]
> This is one of 214 standalone projects, maintained as part
> of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo
> and anti-framework.
>
> 🚀 Please help me to work full-time on these projects by sponsoring me on
> GitHub. Thank you! ❤️
- About
- Status
- Related packages
- Installation
- Dependencies
- Usage examples
- API
- Basic usage
- Graph specification
- Authors
- License
About
Declarative, reactive dataflow graph construction using
@thi.ng/rstream,
@thi.ng/atom
and
@thi.ng/transducers
primitives.
Stream subscription types act as graph nodes and attached transducers as
graph edges, transforming data for downstream consumers / nodes.
Theoretically, allows cycles and is not restricted to DAG topologies,
but care must be taken to avoid CPU hogging if those cycles are causing
synchronous computation loops (it the user's responsibility to avoid
these and keep any cycles async).
Status
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
Related packages
- @thi.ng/dot - Graphviz document abstraction & serialization to DOT format
- @thi.ng/resolve-map - DAG resolution of vanilla objects & arrays with internally linked values
- @thi.ng/rstream-dot - Graphviz DOT conversion of @thi.ng/rstream dataflow graph topologies
Installation
``bash`
yarn add @thi.ng/rstream-graph
ESM import:
`ts`
import * as rsg from "@thi.ng/rstream-graph";
Browser ESM import:
`html`
For Node.js REPL:
`js`
const rsg = await import("@thi.ng/rstream-graph");
Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 1.00 KB
Dependencies
- @thi.ng/api
- @thi.ng/atom
- @thi.ng/checks
- @thi.ng/errors
- @thi.ng/paths
- @thi.ng/resolve-map
- @thi.ng/rstream
- @thi.ng/transducers
Note: @thi.ng/api is in _most_ cases a type-only import (not used at runtime)
Usage examples
Three projects in this repo's
/examples
directory are using this package:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------------------------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 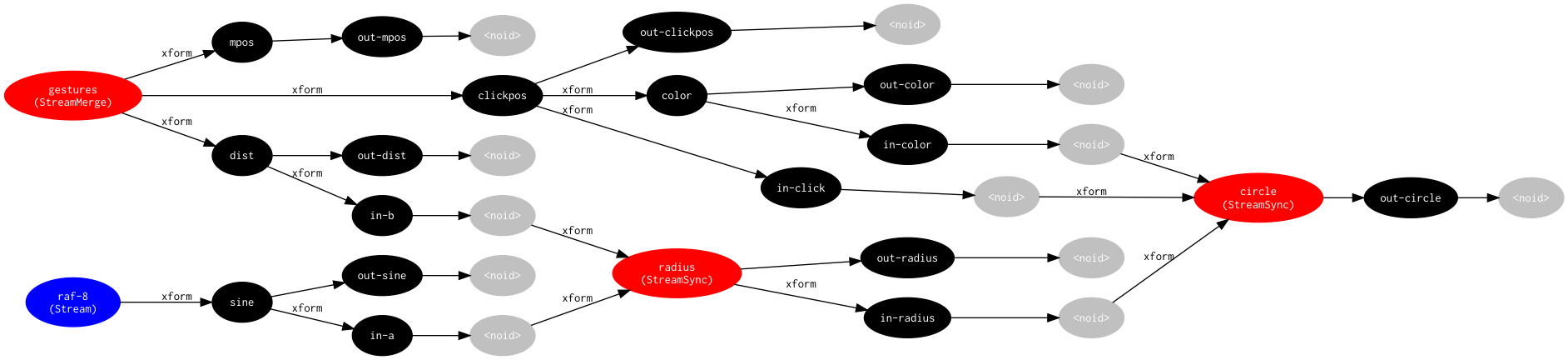 | Minimal rstream dataflow graph | Demo | Source |
| Minimal rstream dataflow graph | Demo | Source |
| 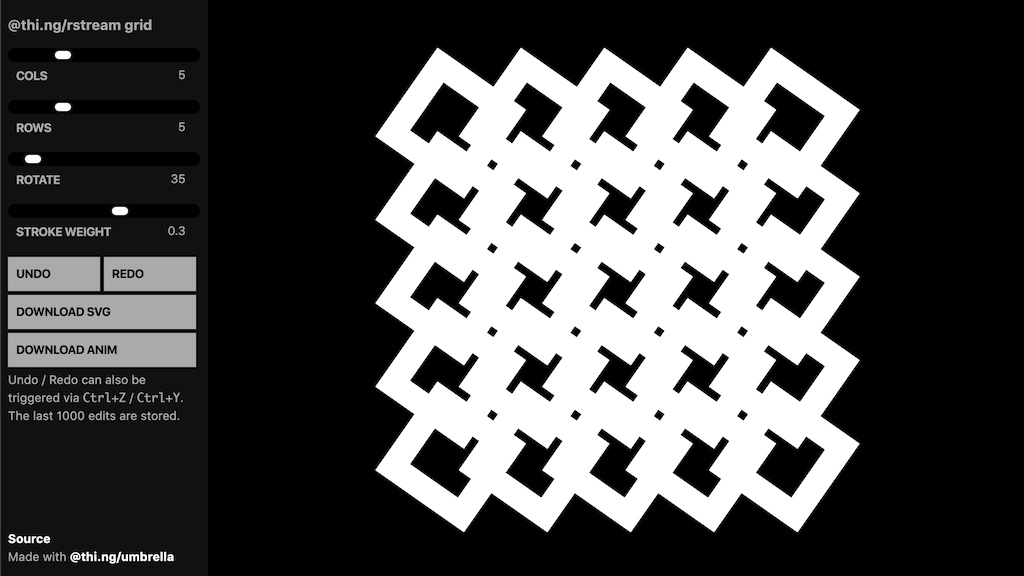 | Interactive grid generator, SVG generation & export, undo/redo support | Demo | Source |
| Interactive grid generator, SVG generation & export, undo/redo support | Demo | Source |
| 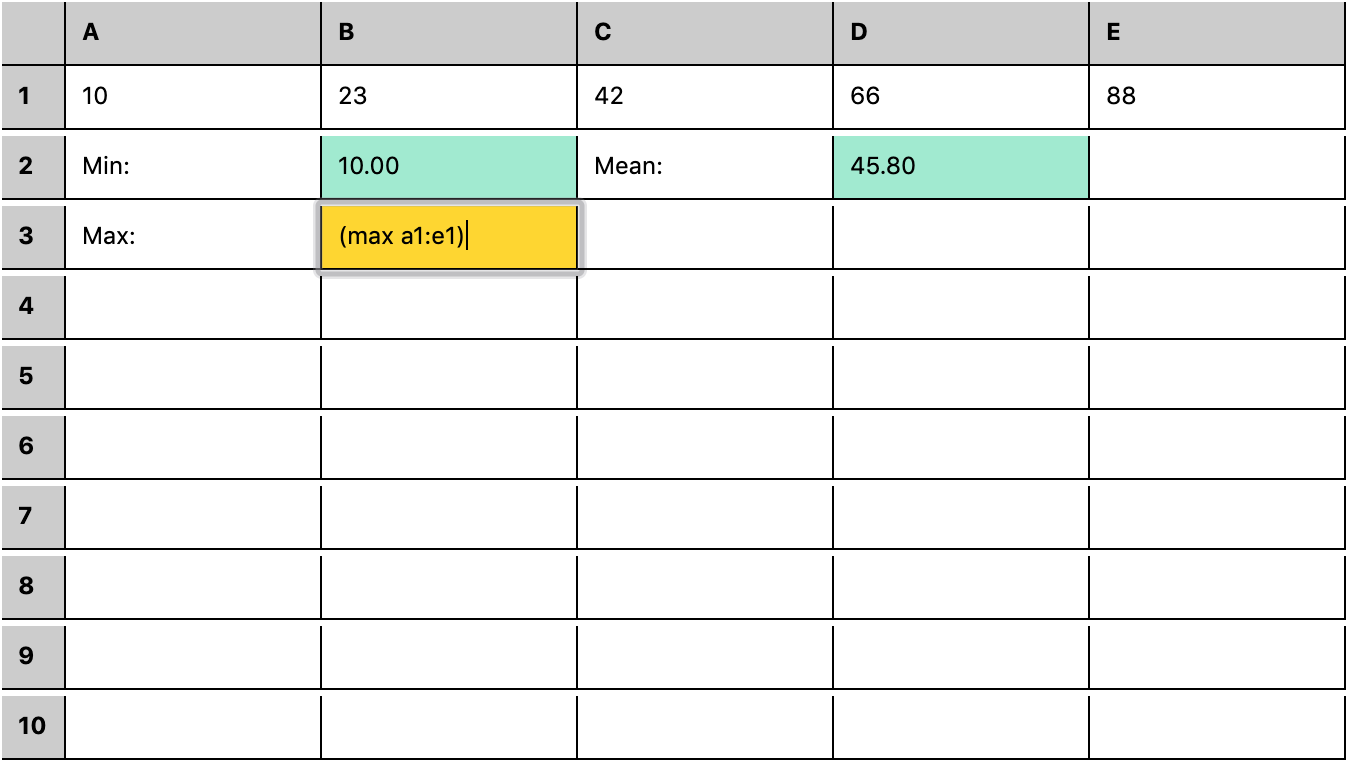 | rstream based spreadsheet w/ S-expression formula DSL | Demo | Source |
| rstream based spreadsheet w/ S-expression formula DSL | Demo | Source |
API
$3
`ts
import { Atom } from "@thi.ng/atom";
import * as rs from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import * as rsg from "@thi.ng/rstream-graph";
// (optional) state atom to source value change streams from
const state = new Atom({a: 1, b: 2});
// graph declaration / definition
const graph = rsg.initGraph(state, {
// this node sources both of its inputs
// from values in the state atom
add: {
fn: rsg.add,
ins: {
a: { path: "a" },
b: { path: "b" }
},
},
// this node receives values from the add node
// and the given iterable
mul: {
fn: rsg.mul,
ins: {
a: { stream: "/add/node" },
b: { stream: () => rs.fromIterable([10, 20, 30]) }
},
}
});
// (optional) subscribe to individual nodes
graph.mul.subscribe({
next: (x) => console.log("result:", x)
});
// result: 30
// result: 60
// result: 90
// changes in subscribed atom values flow through the graph
setTimeout(() => state.resetIn("a", 10), 1000);
// result: 360
`
Graph specification
A dataflow graph spec is a plain object where keys are node names and
their values are NodeSpecs, defining a node's inputs, outputs and the
operation to be applied to produce one or more result streams.
`ts`
interface NodeSpec {
fn: NodeFactory
ins: IObjectOf
outs?: IObjectOf
}
Specification for a single "node" in the dataflow graph. Nodes here are
actually just wrappers of streams / subscriptions (or generally any form
of
@thi.ng/rstream
ISubscribable), usually with an associated transducer to transform /
combine the inputs and produce values for the node's result stream.
The fn function is responsible to produce such a stream transformerins
construct and the library provides several general purpose helpers for
that purpose. The keys used to specify inputs in the object arefn
dictated by the actual node used. Most node functions with multipleStreamSync
inputs will be implemented as
instances and the input IDs are used to locally rename input streams
within the container. Alo see initGraph andnodeFromSpec (in/src/nodes.ts
for more details how these specs are compiled into stream constructs.
Specification for a single input, which can be given in different ways:
1) Create a stream of value changes at given path in state
Atom
(passed to initGraph):
`ts`
{ path: "nested.src.path" }
{ path: ["nested", "src", "path"] }
2) Reference path to another node's output in the GraphSpec object. See
@thi.ng/resolve-map
for details.
`ts`
{ stream: "/node-id/node" } // main node output
{ stream: "/node-id/outs/foo" } // specific output
3) Reference another node indirectly. The passed in resolve function
can be used to lookup other nodes, with the same logic as above. E.g.
the following spec looks up the main output of node "abc" and adds a
transformed subscription, which is then used as input for current
node.
`ts`
{ stream: (resolve) => resolve("/abc/node").map(x => x * 10) }
4) Provide an external input stream:
`ts
import { fromIterable } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
{ stream: () => fromIterable([1,2,3], 500) }
`
5) Single value input stream:
`ts`
{ const: 1 }
{ const: () => 1 }
If the optional xform key is given, a subscription with the given
transducer is added to the input and then used as input instead. This is
allows for further pre-processing of inputs.
Please see detailed documentation in the source code & test cases for
further details.
Authors
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
`bibtex``
@misc{thing-rstream-graph,
title = "@thi.ng/rstream-graph",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/rstream-graph",
year = 2018
}
License
© 2018 - 2026 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0