Periodic callbacks in the background for both IOS and Android
npm install @transistorsoft/capacitor-background-fetch
By Transistor Software, creators of Capacitor Background Geolocation
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Background Fetch is a very simple plugin which attempts to awaken an app in the background about every 15 minutes, providing a short period of background running-time. This plugin will execute your provided callbackFn whenever a background-fetch event occurs.
There is no way to increase the rate which a fetch-event occurs and this plugin sets the rate to the most frequent possible — you will never receive an event faster than 15 minutes. The operating-system will automatically throttle the rate the background-fetch events occur based upon usage patterns. Eg: if user hasn't turned on their phone for a long period of time, fetch events will occur less frequently or if an iOS user disables background refresh they may not happen at all.
> ### :rotating_light: This plugin requires Capacitor 5 :rotating_light:
>
> For Capacitor 4, use the 1.x version of the plugin.
:new: Background Fetch now provides a __scheduleTask__ method for scheduling arbitrary "one-shot" or periodic tasks.
scheduleTask__ seems only to fire when the device is plugged into power.stopOnTerminate: false__ for iOS.-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
``bash`
$ yarn add @transistorsoft/capacitor-background-fetch
$ npx cap sync
bash
$ npm install --save @transistorsoft/capacitor-background-fetch
$ npx cap sync
`- Proceed to Required Setup Guides
Setup Guides
$3
$3
- Nothing else required.
Example ##
:information_source: This repo contains its own Example App. See
#### Angular Example:
- See API Docs __
__`javascript
import { Component } from '@angular/core';import {BackgroundFetch} from '@transistorsoft/capacitor-background-fetch';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: 'home.page.html',
styleUrls: ['home.page.scss'],
})
export class HomePage {
constructor() {}
// Initialize in ngAfterContentInit
// [WARNING] DO NOT use ionViewWillEnter, as that method won't run when app is launched in background.
ngAfterContentInit() {
this.initBackgroundFetch();
}
async initBackgroundFetch() {
const status = await BackgroundFetch.configure({
minimumFetchInterval: 15
}, async (taskId) => {
console.log('[BackgroundFetch] EVENT:', taskId);
// Perform your work in an awaited Promise
const result = await this.performYourWorkHere();
console.log('[BackgroundFetch] work complete:', result);
// [REQUIRED] Signal to the OS that your work is complete.
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
}, async (taskId) => {
// The OS has signalled that your remaining background-time has expired.
// You must immediately complete your work and signal #finish.
console.log('[BackgroundFetch] TIMEOUT:', taskId);
// [REQUIRED] Signal to the OS that your work is complete.
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
});
// Checking BackgroundFetch status:
if (status !== BackgroundFetch.STATUS_AVAILABLE) {
// Uh-oh: we have a problem:
if (status === BackgroundFetch.STATUS_DENIED) {
alert('The user explicitly disabled background behavior for this app or for the whole system.');
} else if (status === BackgroundFetch.STATUS_RESTRICTED) {
alert('Background updates are unavailable and the user cannot enable them again.')
}
}
}
async performYourWorkHere() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(true);
}, 5000);
});
}
}
`Receiving Events After App Termination
- Only Android is able to continue receiving events after app termination. See API Docs __
__.
- For iOS, there is __NO SUCH THING__ as __stopOnTerminate: false__. When an iOS app is terminated, the OS will no longer fire events.Executing Custom Tasks
In addition to the default background-fetch task defined by __
BackgroundFetch.configure__, you may also execute your own arbitrary "oneshot" or periodic tasks (iOS requires additional Setup Instructions). See API Docs __BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask__. However, all events will be fired into the Callback provided to __BackgroundFetch.configure__.$3
- __BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask__ on iOS seems only to run when the device is plugged into power.
- __BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask__ on iOS are designed for low-priority tasks, such as purging cache files — they tend to be unreliable for mission-critical tasks. __BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask__ will never run as frequently as you want.
- The default fetch event is much more reliable and fires far more often.
- __BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask__ on iOS stop when the user terminates the app. There is no such thing as __stopOnTerminate: false__ for iOS.`javascript
// Step 1: Configure BackgroundFetch as usual.
let status = await BackgroundFetch.configure({
minimumFetchInterval: 15
}, async (taskId) => { // <-- Event callback
// This is the fetch-event callback.
console.log("[BackgroundFetch] taskId: ", taskId); // Use a switch statement to route task-handling.
switch (taskId) {
case 'com.foo.customtask':
print("Received custom task");
break;
default:
print("Default fetch task");
}
// Finish, providing received taskId.
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
}, async (taskId) => { // <-- Task timeout callback
// This task has exceeded its allowed running-time.
// You must stop what you're doing and immediately .finish(taskId)
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
});
// Step 2: Schedule a custom "oneshot" task "com.foo.customtask" to execute 5000ms from now.
BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask({
taskId: "com.foo.customtask",
forceAlarmManager: true,
delay: 5000 // <-- milliseconds
});
`
Debugging
$3
#### :new:
API for iOS 13+- :warning: At the time of writing, the new task simulator does not yet work in Simulator; Only real devices. Use Old BackgroundFetch API so simulate events in Simulator.
- See Apple docs Starting and Terminating Tasks During Development
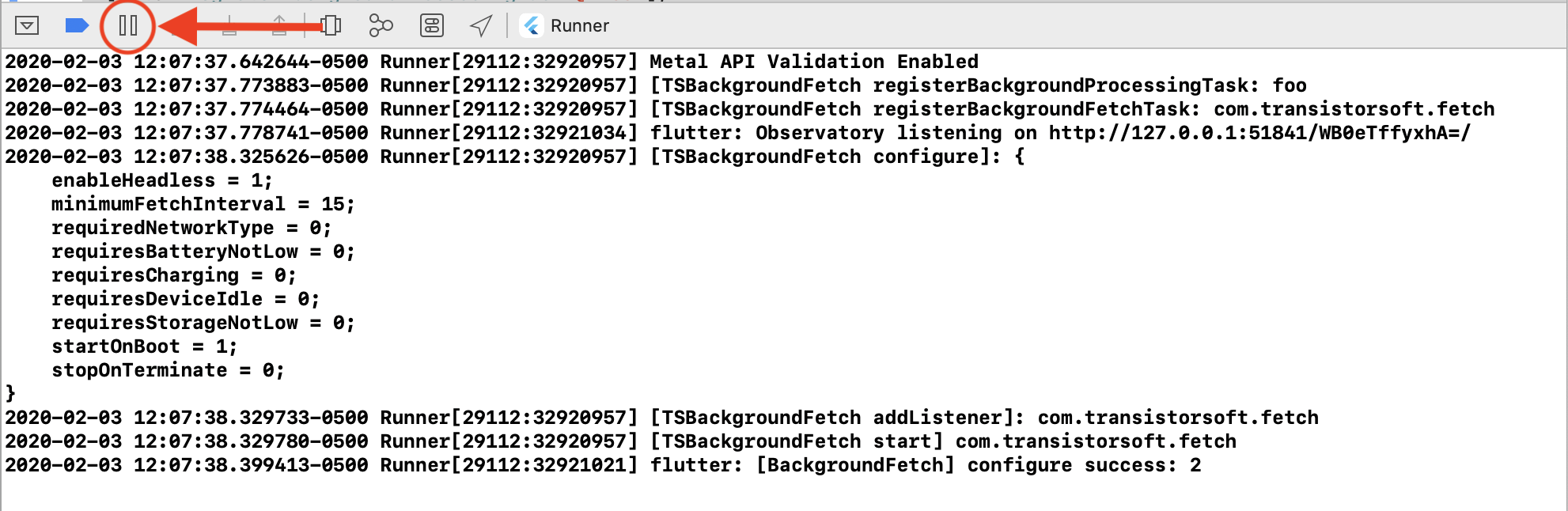
- After running your app in XCode, Click the
[||] button to initiate a Breakpoint.
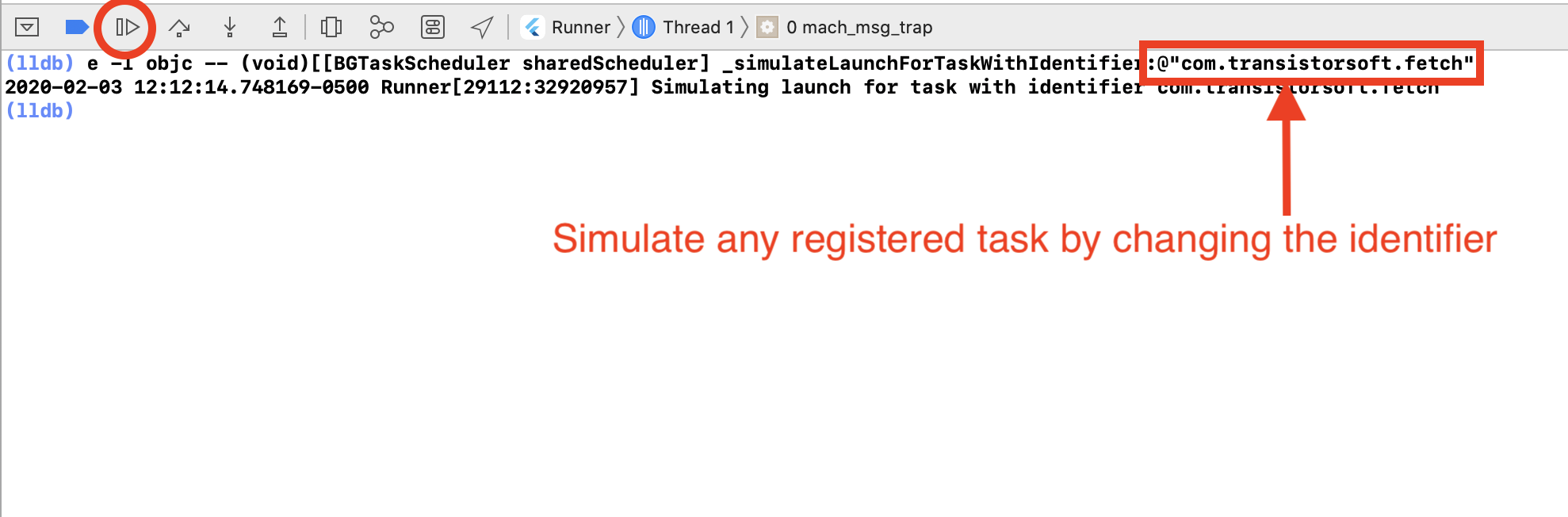
- In the console (lldb), paste the following command (Note: use cursor up/down keys to cycle through previously run commands):
`obj-c
e -l objc -- (void)[[BGTaskScheduler sharedScheduler] _simulateLaunchForTaskWithIdentifier:@"com.transistorsoft.fetch"]
`
- Click the button to continue. The task will execute and the Callback function provided to __BackgroundFetch.configure__ will receive the event.
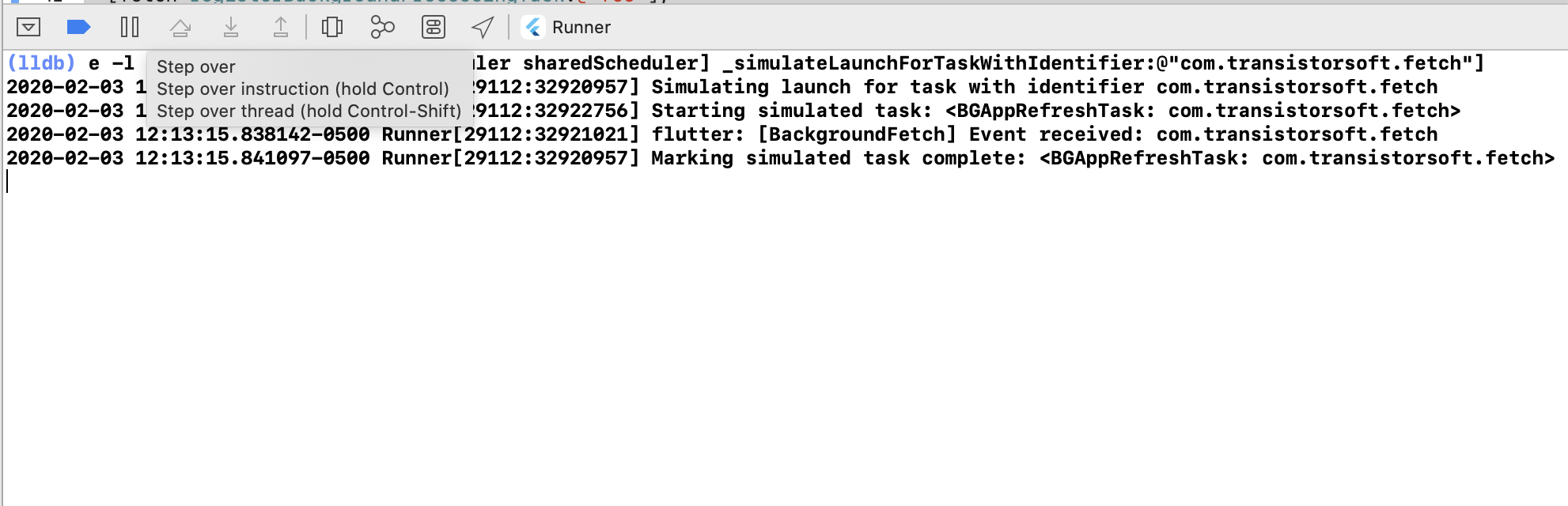
#### Simulating task-timeout events
- Only the new
BGTaskScheduler api supports simulated task-timeout events. To simulate a task-timeout, your fetchCallback must not call __BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId)__:`javascript
const status = await BackgroundFetch.configure({
minimumFetchInterval: 15
}, async (taskId) => { // <-- Event callback.
// This is the task callback.
console.log("[BackgroundFetch] taskId", taskId);
//BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId); // <-- Disable .finish(taskId) when simulating an iOS task timeout
}, async (taskId) => { // <-- Event timeout callback
// This task has exceeded its allowed running-time.
// You must stop what you're doing and immediately .finish(taskId)
console.log("[BackgroundFetch] TIMEOUT taskId:", taskId);
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
});
`- Now simulate an iOS task timeout as follows, in the same manner as simulating an event above:
obj-c
e -l objc -- (void)[[BGTaskScheduler sharedScheduler] _simulateExpirationForTaskWithIdentifier:@"com.transistorsoft.fetch"]
`#### Old
API
- Simulate background fetch events in XCode using Debug->Simulate Background Fetch
- iOS can take some hours or even days to start a consistently scheduling background-fetch events since iOS schedules fetch events based upon the user's patterns of activity. If Simulate Background Fetch works, your can be sure that everything is working fine. You just need to wait.$3
- Observe plugin logs in
:`bash
$ adb logcat *:S TSBackgroundFetch:V Capacitor/Console:V Capacitor/Plugin:V
`- Simulate a background-fetch event on a device (insert <your.application.id>) (only works for sdk
:
`bash
$ adb shell cmd jobscheduler run -f 999
`
- For devices with sdk , simulate a "Headless JS" event with (insert <your.application.id>)
`bash
$ adb shell am broadcast -a .event.BACKGROUND_FETCH ``The MIT License
Copyright (c) 2013 Chris Scott, Transistor Software
http://transistorsoft.com
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.