concent
v2.21.12TypeScript
Build-in dependency collection, a predictable、zero-cost-use、progressive、high performance's react develop framework
reactreact control centerconcentstate managementstate syncstate broadcaststate dispatchwork with reduxreplace redux
0/weekUpdated 1 months agoMITUnpacked: 1.7 MB
Published by fantasticsoul
npm install concentEnglish | 简体中文
concent
❤️ 内置依赖收集,一个可预测、0入侵、渐进式、高性能的react开发框架!
了解更多请访问官方文档https://concentjs.github.io/concent-doc.
!hello-concent
📦快速开始
确保已安装nodejs。
$3
使用npm命令安装
concent``sh`
$ cd cc-app
$ npm i --save concent
or yarn command
`sh`
$ yarn add concent
$3
使用run
接口定义一个模块`js
import { run } from 'concent';run({
counter: {// 声明一个名为'counter'的模块
state: { num: 1, numBig: 100 }, // 定义状态
},
// 你也可以在这里继续声明或添加其他模块
});
`$3
使用接口为class组件指定一个模块,或useConcent为function组件指定一个模块。
> 让concent知道当前组件属于具体的哪个模块`js
import { register, useConcent } from 'concent';@register('counter')
class DemoCls extends React.Component{
// 此时setState提交的状态触发自己重渲染
// 同时也会触发其他同样属于counter模块的实例且消费了具体数据的实例重渲染
inc = ()=> this.setState({num: this.state.num + 1})
render(){
// 这里读取了num,意味着当前实例的依赖key列表是 ['num']
const { num } = this.state;
// render logic
}
}
function DemoFn(){
const { state, setState } = useConcent('counter');
const inc = ()=> setState({num: state.num + 1});
// render logic
}
`注意
是一个proxy对象,用于帮助concent在组件实例在每一轮渲染期间动态的收集到依赖列表,让精确渲染得以优雅实现。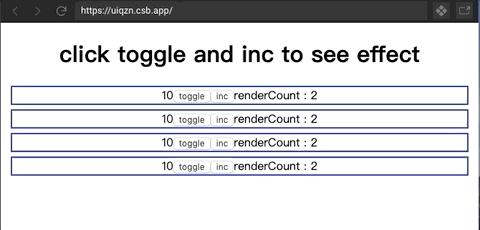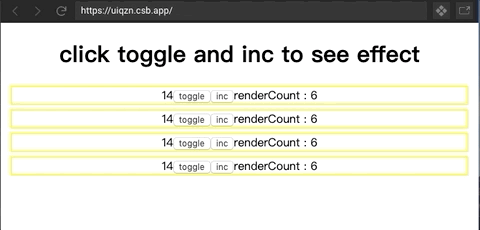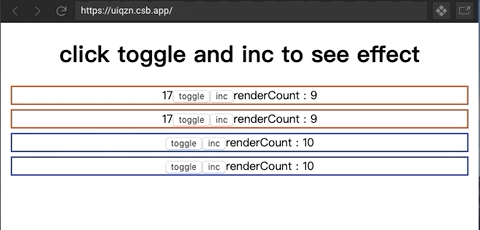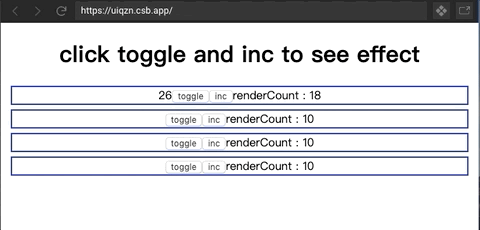
$3
实例化concent组件不需要任何Provider包裹在根节点处,你可以在任何地方做实例化,查看在线演示`jsx
const rootElement = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(
rootElement
);
`$3
如果你在改变状态状态之前还有很多业务逻辑要处理,推荐将它们剥离到
> 为了concent获得最佳的运行性能,强调用户总是返回片段状态。js
run({
counter: {
state: {/* ... /},
reducer: {
inc(payload, moduleState) {
return { num: moduleState.num + 1 };
},
async asyncInc(payload, moduleState) {
await delay();
return { num: moduleState.num + 1 };
},
},
},
});
`定义完
之后,你可以在组件里呼叫定义好的方法了,从而替代setStatejs
// --------- 对于类组件 -----------
changeNum = () => this.setState({ num: 10 })
// ===> 修改为
changeNum = () => this.ctx.mr.inc(10);// or this.ctx.mr.asynInc(10)//当然这里也可以写为ctx.dispatch调用,不过更推荐用上面的moduleReducer直接调用
//this.ctx.dispatch('inc', 10); // or this.ctx.dispatch('asynInc', 10)
// --------- 对于函数组件 -----------
const { state, mr } = useConcent("counter");// useConcent 返回的就是ctx
const changeNum = () => mr.inc(20); // or ctx.mr.asynInc(10)
//对于函数组将同样支持dispatch调用方式
//ctx.dispatch('inc', 10); // or ctx.dispatch('asynInc', 10)
`在脱离ui范围的时候,
允许用户使用顶层api修改状态。- 使用
setState `js
import { getState, setState } from "concent";console.log(getState('counter').num);// log: 1
setState('counter', {num:10});// 修改counter模块num值
console.log(getState('counter').num);// log: 10
`- 使用
dispatch 会返回一个promise,所以我们需要在外部包裹一个asyncjs
import { getState, dispatch } from "concent";(async ()=>{
console.log(getState("counter").num);// log 1
await dispatch("counter/inc");
console.log(getState("counter").num);// log 2
await dispatch("counter/asyncInc");
console.log(getState("counter").num);// log 3
})()
`- 使用
run接口定义的reducer集合已被concent集中管理起来,并允许用户以reducer.${moduleName}.${methodName}的方式直接发起调用`js
import { getState, reducer as ccReducer } from "concent";(async ()=>{
console.log(getState("counter").num);// log 1
await ccReducer.counter.inc();
console.log(getState("counter").num);// log 2
await ccReducer.counter.asyncInc();
console.log(getState("counter").num);// log 3
})()
`$3
如果你想基于模块状态计算出其他数据,推荐定义js
run({
counter: {
state: { /* ... /},
reducer: { /* ... /},
computed: {
numx2: ({num})=> num * 2,
numBigx2: ({numBig})=> numBig * 2,
numSumBig: ({num, numBig})=> num + numBig,
},
},
});// 函数组件ui处获取计算结果
const { moduleComputed } = useConcent('counter');
// 类组件ui处获取计算结果
const { moduleComputed } = this.ctx;
`注意当你在函数的参数列表里解构具体的值时,也是在同时声明了当前计算函数的依赖。
js
// 当前函数仅在num或者numBig发送改变时才会触发重计算
const numSumBig = ({num, numBig})=> num + numBig,
`
async comoputed 也是支持的, 点击查看演示.
🖥在线体验
- 快速开始:
快速了解和上手concent的强大特性!!
- todo app:
下面还有一个链接使用hook&redux编写,可以点击查看并感受concent版本和hook&redux版本的差异
> 使用hook&redux编写 (author:Gábor Soós@blacksonic)
- 结合了concent生态库的企业级项目模板(js):
- 结合了concent生态库的企业级项目模板(ts):
source code see here:https://github.com/fantasticsoul/concent-guid-ts✨特性
* 极简的核心api,载入模块配置启动concent,register注册组件,无需包一层Provider在根组件。
* 0入侵成本接入,不改造代码的情况下直接接入;hello-concent
* 贴心的模块配置,除了state,还提供reducer、computed、watch和init四项可选定义。
* 灵活的数据消费粒度,支持跨多个模块场景,以及模块内stateKey级别的细粒度控制。
* 渐进式构建react应用,除了setState,支持dispatch、invoke调用来让ui视图与业务逻辑彻底解耦。从class到function
* 组件能力增强,支持实例级别computed、watch定义,支持emit&on,以及支持setup特性,让函数组件拥有定义静态api的能力。
* 高度一致的编程体验,hoc、render props和hook3种方式定义的组件均享有一致的api调用体验,相互切换代价为0。多种方式定义组件
* 渲染性能出众,内置renderKey、lazyDispatch、delayBroadcast等特性,保证极速的渲染效率。长列表精准渲染、批处理状态提交、高频输入场景状态延迟分发
* 干净的dom层级,对于class组件,默认采用反向继承策略,让react dom树的层级结构保持简洁与干净。
* 扩展中间件与插件,允许用户定义中间件拦截所有的数据变更提交记录,做额外处理,也可以自定义插件,接收运行时的发出的各种信号,按需增强concent自身的能力。
* 去中心化配置模块,除了run接口一次性配置模块,还提供configure接口在任意地方动态配置模块。
* 模块克隆,支持对已定义模块进行克隆,满足你高维度抽象的需要。
* 完整的typescript支持,能够非常容易地书写优雅的ts代码。$3
$3
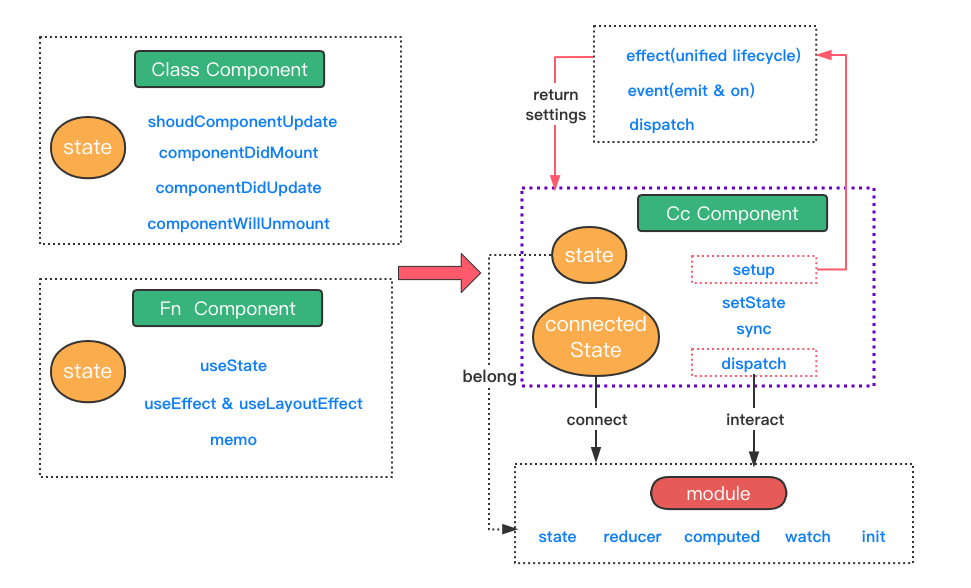Eco system
基于中间件和插件机制,你可以很容易的抽象和定制非业务相关的处理器,或者迁移redux生态相关库。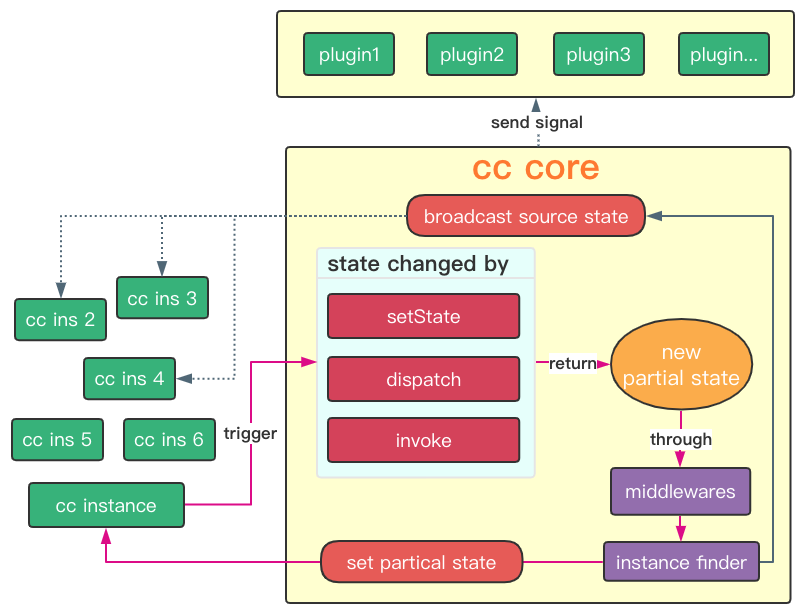
搭配react-router使用
请移步阅读和了解react-router-concent,暴露history对象,可以全局任意地方使用,享受编程式的导航跳转。搭配redux-dev-tool使用
请移步阅读和了解concent-plugin-redux-devtool,全流程追溯你的状态变更过程。
!redux-dev-tool搭配loading插件使用
请移步阅读和了解concent-plugin-loading,轻松控制concent应用里所有reducer函数的loading状态。❤️依赖收集
concent使用Proxy&defineProperty in v2.3+完成了运行时的依赖收集特性,大幅缩小UI视图渲染范围,提高应用性能。$3
`js
run({
counter:{
state:{
modCount: 10,
modCountBak: 100,
factor: 1,
},
computed:{
xxx(n){
return n.modCount + n.modCountBak;
},// for xxx computed retKey, the depKeys is ['modCount', 'modCountBak']
yyy(n){
return n.modCountBak;
},// for yyy computed retKey, the depKeys is ['modCountBak']
zzz(n, o, f){// n means newState, o means oldState, f means fnCtx
return f.cuVal.xxx + n.factor;
},// for zzz computed retKey, the depKeys is ['factor', 'modCount', 'modCountBak']
},
watch:{
xxx:{
fn(n){
console.log('---> trigger watch xxx', n.modCount);
},// for xxx watch retKey, the depKeys is ['modCount']
immediate: true,
},
}
}
});
`$3
js
const setup = ctx => {
ctx.computed('show', (n)=>{
return n.show + n.cool + n.good;
});// for show retKey, the depKeys is ['show', 'cool', 'good'] ctx.computed('show2', (n)=>{
return n.show + '2222' + n.cool;
});// for show2 retKey, the depKeys is ['show', 'cool', 'good']
};
`$3
js
import {register, useConcent} from 'concent';const iState = ()=>({show:true});
function FnComp(){
const {state, syncBool} = useConcent({module:'counter', state:iState, setup});
return (
{/* if show is true, current ins's dependency is ['modCount']/}
{state.show? {state.modCount} : ''}
);
}@register({module:'counter', state:iState, setup})
class ClassComp extends React.Component{
// state = iState(); //or write private state here
render(){
const {state, syncBool} = this.ctx;
return (
{/* if show is true, current ins's dependency is ['modCount']/}
{state.show? {state.modCount} : ''}
}
}
`
edit this demo on CodeSandbox🔨代码实战
- 运行concent,载入模块配置javascript
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
import { register, run } from 'concent';run({
counter: {// 定义counter模块
state: {// 【必需】,定义state
count: 0,
products: [],
type: '',
},
reducer: {// 【可选】定义reducer,书写修改模块状态逻辑
inc(payload=1, moduleState) {
return { count: moduleState.count + payload };
},
dec(payload=1, moduleState) {
return { count: moduleState.count - payload };
},
async inc2ThenDec3(payload, moduleState, actionCtx){
await actionCtx.dispatch('inc', 2);
await actionCtx.dispatch('dec', 3);
}
},
computed:{// 【可选】定义模块computed,当对应的stateKey发生变化时触发计算函数,结果将被缓存
count(newState, oldState){
return newState.count * 2;
}
},
watch:{// 【可选】定义模块watch,当对应的stateKey发生变化时触发watch函数,通常用于触发一些异步任务的执行
count(newState, oldState){
console.log(
count changed from ${oldState.count} to ${newState.count});
}
},
init: async ()=>{// 【可选】模块状态的初始化函数,当状态需要异步的定义,且与具体挂载的组件无关时定义此项
const state = await api.fetchState();
return state;
}
}
})
`
更推荐将模块定义选项放置到各个文件中,然后在各自导出交给函数配置.
`
|____models # business models
| |____index.js
| |____counter
| | |____index.js
| | |____reducer.js # change state methods(optional)
| | |____computed.js # computed methods(optional)
| | |____watch.js # watch methods(optional)
| | |____init.js # async state initialization function(optional)
| | |____state.js # module init state(required)
此时reducer文件里函数可以不需要基于字符串发起组合型调用了
js
export function inc(payload=1, moduleState) {
return { count: moduleState.count + payload };
}export function dec(payload=1, moduleState) {
return { count: moduleState.count - payload };
}
// 组合调用其他的reducer函数完成业务逻辑
export async function inc2ThenDec3(payload, moduleState, actionCtx){
await actionCtx.dispatch(inc, 2);
await actionCtx.dispatch(dec, 3);
}
`
当然reducer文件里,你可以调用setState,是一个被promise话的句柄
js
export updateLoading(loading){
return { loading }
}export async function inc2ThenDec3(payload, moduleState, actionCtx){
await actionCtx.dispatch(inc, 2);
//等效于调用actionCtx.dispatch(updateLoading, true);
await actionCtx.setState({loading: true});
await actionCtx.dispatch(dec, 3);
//等效于调用actionCtx.dispatch(updateLoading, false);
await actionCtx.setState({loading: false});
//最后这里你可以选择的返回一个新的片断状态,也会触发视图更新
return { tip: 'you can return some new value in current reducer fn ot not' };
}
`- 定义 setup
只会在初次渲染之前被执行一次,同样用于定义一些副作用函数,或者一些随后可以在渲染函数体内通过ctx.settings取到的方法,所以将不在产生大量的临时闭包函数,且setup可以同时传递给类组件和函数组件,意味着你可以随时地切换组件形态,优雅的复用业务逻辑。
`js
const setup = ctx => {
console.log('setup函数只会在组件初次渲染之前被执行一次');
ctx.on('someEvent', (p1, p2)=> console.log('receive ', p1, p2)); ctx.effect(() => {
fetchProducts();
}, ["type", "sex", "addr", "keyword"]);//这里只需要传key名称就可以了
/** 原函数组件内写法:
useEffect(() => {
fetchProducts(type, sex, addr, keyword);
}, [type, sex, addr, keyword]);
*/
ctx.effect(() => {
return () => {
// 返回一个清理函数
// 等价于componentWillUnmout, 这里搞清理事情
};
}, []);
/** 原函数组件内写法:
useEffect(()=>{
return ()=>{// 返回一个清理函数
// 等价于componentWillUnmout, 这里搞清理事情
}
}, []);//第二位参数传空数组,次副作用只在初次渲染完毕后执行一次
*/
ctx.effectProps(() => {
// 对props上的变更书写副作用,注意这里不同于ctx.effect,ctx.effect是针对state写副作用
const curTag = ctx.props.tag;
if (curTag !== ctx.prevProps.tag) ctx.setState({ tag: curTag });
}, ["tag"]);//这里只需要传key名称就可以了
/** 原函数组件内写法:
useEffect(()=>{
// 首次渲染时,此副作用还是会执行的,在内部巧妙的再比较一次,避免一次多余的ui更新
// 等价于类组件里getDerivedStateFromProps里的逻辑
if(tag !== propTag)setTag(tag);
}, [propTag, tag]);
*/
// 定义实例计算函数,当count值变化时会触发其计算,用户可随后在渲染函数体内通过ctx.refComputed.doubleTen获得计算结果
ctx.computed('doubleTen', (newState, oldState)=>{
return newState.count * 10;
}, ['count']);
// 大多数情况你应该首先考虑定义模块计算函数,如果你想所有实例共享计算逻辑且计算函数只被执行一次,因为对于实例计算函数来说是每个实例都会自己单独触发的
// 如果结果key和状态key命名一样,可简写为如下格式
ctx.computed('count', ({count})=>count*2);
// 定义实例观察函数, 和模块计算的理由一样,你应该优先考虑定义模块模块级别的观察函数
ctx.watch('retKey', ()=>{}, ['count']);
const fetchProducts = () => {
const { type, sex, addr, keyword } = ctx.state;
api.fetchProducts({ type, sex, addr, keyword })
.then(products => ctx.setState({ products }))
.catch(err => alert(err.message));
};
const inc = () => {
ctx.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}
const dec = () => {
ctx.setState({ count: this.state.count - 1 });
}
// 通过dispatch触发reducer函数
const incD = () => {
ctx.dispatch('inc');// 也可以写为: this.ctx.moduleReducer.inc()
}
const decD = () => {
ctx.dispatch('dec');// 也可以写为: this.ctx.moduleReducer.dec()
}
// 返回结果将收集ctx.settings里
return {
inc,
dec,
incD,
decD,
fetchProducts,
//同步type值, sync能够自动提取event事件里的值
changeType: ctx.sync('type'),
};
};
`- 基于
、renderProps, hook3种方式注册为concent组件
`jsx
@register({module:'counter', setup})
class Counter extends Component {
constructor(props, context){
super(props, context);
this.state = {tag: props.tag};// 私有状态
}
render() {
// 此时的state由私有状态和模块状态合并而得
const { count, products, tag } = this.state;
// this.state 也可以写为 this.ctx.state
//const { count, products, tag } = this.ctx.state; const {inc, dec, indD, decD, fetchProducts, changeType} = this.ctx.settings;
return 'your ui xml...';
}
}
const PropsCounter = registerDumb({module:'counter', setup})(ctx=>{
const { count, products, tag } = ctx.state;
const {inc, dec, indD, decD, fetchProducts, changeType} = ctx.settings;
return 'your ui xml...';
});
function HookCounter(){
const ctx = useConcent({module:'counter', setup});
const { count, products, tag } = ctx.state;
const {inc, dec, indD, decD, fetchProducts, changeType} = ctx.settings;
return 'your ui xml...';
}
``⚖️在线比较
* concent代办列表mvc vs redux&hook代办列表mvc
* 基于concent的计算器 vs 基于hook的计算器
* 基于concent的查询列表& 基于concent的共享状态查询列表 vs 基于hook的查询列表
💻在线示例
* 渐进式的开发react应用
* 有趣的counter
* stackblitz示例集合
* run api demo
⌨️在线git
* concent ant-design-pro
📰图文收集
* redux、mobx、concent特性大比拼, 看后生如何对局前辈
* 聊一聊状态管理&Concent设计理念
* 应战Vue3 setup,Concent携手React出招了!
* 深度挖掘Concent的effect,全面提升useEffect的开发体验
* concent 骚操作之组件创建&状态更新
* 使用concent,体验一把渐进式地重构react应用之旅
___
图片介绍
$3