epicfail
v3.0.0TypeScript
Better error output for Node.js CLI apps
0/weekUpdated 3 years agoApache-2.0Unpacked: 258.1 KB
Published by Yasuaki Uechi
npm install epicfailepicfail
Better error reporting for Node.js command-line apps.
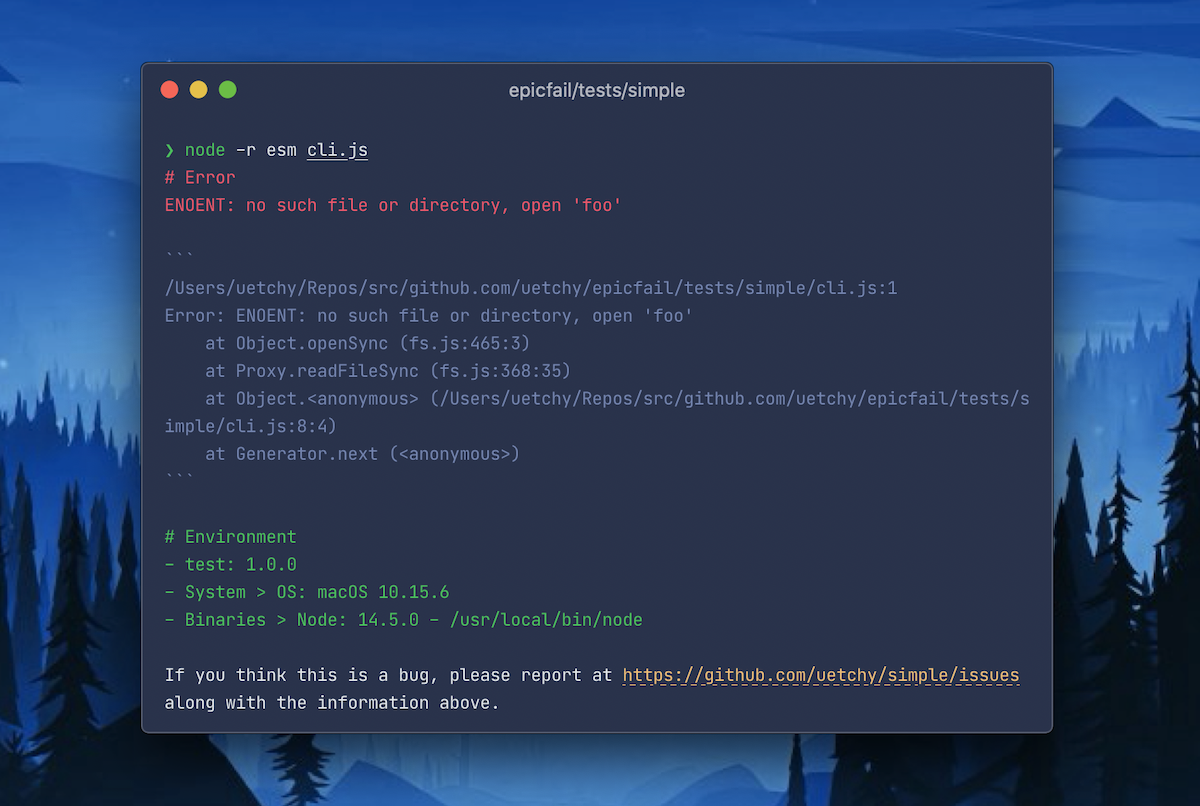
Features
[![npm-version]][npm-url]
[![npm-downloads]][npm-url]
!npm bundle size

[npm-version]: https://badgen.net/npm/v/epicfail
[npm-downloads]: https://badgen.net/npm/dt/epicfail
[npm-url]: https://npmjs.org/package/epicfail
> epicfail converts unhandledRejection and uncaughtException into graceful and helpful error message for both users and developers.
⬇️ Prints error messages in _copy and paste ready_ Markdown.
🌐 Asks users to report a bug (navigate users to bugs.url in package.json).
🍁 Shows machine environments (OS, Node.js version, etc).
👀 Suggests related issues in GitHub.
🛠 Integration with error aggregation service (like Sentry).
Table of Contents
- epicfail
- Features
- Table of Contents
- Install
- Use
- ESModules
- CommonJS
- Options
- stacktrace (default: true)
- issues (default: false)
- env
- message (default: true)
- assertExpected (default: () => false)
- onError (default: undefined)
- Advanced Usage
- Print error message without extra information
- Sentry integration
- Runtime options
Install
``bash`
npm install --save epicfailor
yarn add epicfail
Use
$3
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url);
// your CLI app code goes here
fs.readFileSync("foo"); // => will cause "ENOENT: no such file or directory, open 'foo'"
`
$3
`js
const { epicfail } = require("epicfail");
epicfail(require.main.filename);
// your CLI app code goes here
fs.readFileSync("foo"); // => will cause "ENOENT: no such file or directory, open 'foo'"
`
Options
$3
Show stack trace.
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url, {
stacktrace: false,
});
`
$3
Search and show related issues in GitHub Issues.
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url, {
issues: true,
});
`
$3
Show environment information. You can find all possible options here. Set to false to disable it.
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url, {
env: {
System: ["OS", "CPU"],
Binaries: ["Node", "Yarn", "npm"],
Utilities: ["Git"],
},
});
`
Default values:
`json`
{
"System": ["OS"],
"Binaries": ["Node"]
}
$3
Show bug tracker URL and ask users to report the error.
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url, { message: false });
`
$3
While processing an error, if assertExpected(error) returns true, epicfail just prints the error message without any extra information; which is the same behaviour as the logAndExit() function described below.
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url, {
assertExpected: (err) => err.name === "ArgumentError",
});
`
$3
Pass the function that process the error and returns event id issued by external error aggregation service.
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
import Sentry from "@sentry/node";
epicfail(import.meta.url, {
onError: (err) => Sentry.captureException(err), // will returns an event id issued by Sentry
});
`
Advanced Usage
$3
Use logAndExit() to print error message in red text without any extra information (stack trace, environments, etc), then quit program. It is useful when you just want to show the expected error message without messing STDOUT around with verbose log messages.
`js
import { epicfail, logAndExit } from "epicfail";
epicfail(import.meta.url);
function cli(args) {
if (args.length === 0) {
logAndExit("usage: myapp ");
}
}
cli(process.argv.slice(2));
`
You can also pass an Error instance:
`js`
function cli(args) {
try {
someFunction();
} catch (err) {
logAndExit(err);
}
}
$3
`js
import { epicfail } from "epicfail";
import Sentry from "@sentry/node";
epicfail(import.meta.url, {
stacktrace: false,
env: false,
onError: Sentry.captureException, // will returns event_id issued by Sentry
});
Sentry.init({
dsn: "
defaultIntegrations: false, // required
});
// your CLI app code goes here
fs.readFileSync("foo"); // => will cause "ENOENT: no such file or directory, open 'foo'"
`
$3
`js
import {epicfail} from 'epicfail';
epicfail(import.meta.url);
// 1. Use epicfail property in Error instance.
const expected = new Error('Wooops');
expected.epicfail = { stacktrace: false, env: false, message: false };
throw expected;
// 2. Use fail method
import { fail } from 'epicfail';
fail('Wooops', { stacktrace: false, env: false, message: false });
// 3. Use EpicfailError class (useful in TypeScript)
import { EpicfailError } from 'epicfail';
const err = new EpicfailError('Wooops', { stacktrace: false, env: false, message: false };);
throw err;
``