ghost-cursor
v1.4.2TypeScript
Move your mouse like a human in puppeteer or generate realistic movements on any 2D plane
0/weekUpdated 3 weeks agoISCUnpacked: 95.2 KB
Published by Xetera
npm install ghost-cursorGhost Cursor

Generate realistic, human-like mouse movement data between coordinates or navigate between elements with puppeteer
like the definitely-not-robot you are.
> Oh yeah? Could a robot do _this?_
Installation
``sh`
yarn add ghost-cursor
or with npmsh`
npm install ghost-cursor
Usage
Generating movement data between 2 coordinates.
`js
import { path } from "ghost-cursor"
const from = { x: 100, y: 100 }
const to = { x: 600, y: 700 }
const route = path(from, to)
/**
* [
* { x: 100, y: 100 },
* { x: 108.75573501957051, y: 102.83608396351725 },
* { x: 117.54686481838543, y: 106.20019239793275 },
* { x: 126.3749821408895, y: 110.08364505509256 },
* { x: 135.24167973152743, y: 114.47776168684264 }
* ... and so on
* ]
*/
`
Generating movement data between 2 coordinates with timestamps.
`js
import { path } from "ghost-cursor"
const from = { x: 100, y: 100 }
const to = { x: 600, y: 700 }
const route = path(from, to, { useTimestamps: true })
/**
* [
* { x: 100, y: 100, timestamp: 1711850430643 },
* { x: 114.78071695023473, y: 97.52340709495319, timestamp: 1711850430697 },
* { x: 129.1362373468682, y: 96.60141853603243, timestamp: 1711850430749 },
* { x: 143.09468422606352, y: 97.18676354029148, timestamp: 1711850430799 },
* { x: 156.68418062398405, y: 99.23217132478408, timestamp: 1711850430848 },
* ... and so on
* ]
*/
`
Usage with puppeteer:
`js
import { GhostCursor } from "ghost-cursor"
import puppeteer from "puppeteer"
const run = async (url) => {
const selector = "#sign-up button"
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({ headless: false });
const page = await browser.newPage()
const cursor = new GhostCursor(page)
await page.goto(url)
await page.waitForSelector(selector)
await cursor.click(selector)
// shorthand for
// await cursor.move(selector)
// await cursor.click()
}
`
$3
* cursor.move()
will automatically overshoot or slightly miss and re-adjust for elements that are too far away
from the cursor's starting point.
* When moving over objects, a random coordinate that's within the element will be selected instead of
hovering over the exact center of the element.
* The speed of the mouse will take the distance and the size of the element you're clicking on into account.
> Ghost cursor in action on a form
Methods
####
new GhostCursor(page: puppeteer.Page, { start?: Vector, performRandomMoves?: boolean, defaultOptions?: DefaultOptions, visible?: boolean = false }): GhostCursorCreates the ghost cursor that contains the action functions described below.
- page: Puppeteer
.
- start (optional): Cursor start position. Default is { x: 0, y: 0 }.
- performRandomMoves (optional): Initially perform random movements. Default is false.
- defaultOptions (optional): Set custom default options for click, move, moveTo, and randomMove functions. Default values are described below.
- visible (optional): Make the cursor visible, using installMouseHelper(). Default is false.
#### toggleRandomMove(random: boolean): voidToggles random mouse movements on or off.
####
Simulates a mouse click at the specified selector or element.
- selector (optional): CSS selector or ElementHandle to identify the target element.
- options (optional): Additional options for clicking. Extends the
of the move, scrollIntoView, and getElement functions (below)
- hesitate (number): Delay before initiating the click action in milliseconds. Default is 0.
- waitForClick (number): Delay between mousedown and mouseup in milliseconds. Default is 0.
- moveDelay (number): Delay after moving the mouse in milliseconds. Default is 2000. If randomizeMoveDelay=true, delay is randomized from 0 to moveDelay.
- button (MouseButton): Mouse button to click. Default is left.
- clickCount (number): Number of times to click the button. Default is 1.####
move(selector: string | ElementHandle, options?: MoveOptions): PromiseMoves the mouse to the specified selector or element.
- selector: CSS selector or ElementHandle to identify the target element.
- options (optional): Additional options for moving. Extends the
of the scrollIntoView and getElement functions (below)
- paddingPercentage (number): Percentage of padding to be added inside the element when determining the target point. Default is 0 (may move to anywhere within the element). 100 will always move to center of element.
- destination (Vector): Destination to move the cursor to, relative to the top-left corner of the element. If specified, paddingPercentage is not used. If not specified (default), destination is random point within the paddingPercentage.
- moveDelay (number): Delay after moving the mouse in milliseconds. Default is 0. If randomizeMoveDelay=true, delay is randomized from 0 to moveDelay.
- randomizeMoveDelay (boolean): Randomize delay between actions from 0 to moveDelay. Default is true.
- maxTries (number): Maximum number of attempts to mouse-over the element. Default is 10.
- moveSpeed (number): Speed of mouse movement. Default is random.
- overshootThreshold (number): Distance from current location to destination that triggers overshoot to occur. (Below this distance, no overshoot will occur). Default is 500.####
moveTo(destination: Vector, options?: MoveToOptions): PromiseMoves the mouse to the specified destination point.
- destination: An object with
and y coordinates representing the target position. For example, { x: 500, y: 300 }.
- options (optional): Additional options for moving.
- moveSpeed (number): Speed of mouse movement. Default is random.
- moveDelay (number): Delay after moving the mouse in milliseconds. Default is 0. If randomizeMoveDelay=true, delay is randomized from 0 to moveDelay.
- randomizeMoveDelay (boolean): Randomize delay between actions from 0 to moveDelay. Default is true.####
moveBy(delta: Vector, options?: MoveToOptions): PromiseMoves the mouse by a specified amount.
- delta: An object with
and y coordinates representing the distance to move. For example, { x: 10, y: 20 }.
- options (optional): Additional options for moving. Same as moveTo options
#### scrollIntoView(selector: string | ElementHandle, options?: ScrollIntoViewOptions) => PromiseScrolls the element into view. If already in view, no scroll occurs.
- selector: CSS selector or ElementHandle to identify the target element.
- options (optional): Additional options for scrolling. Extends the
of the getElement and scroll functions (below)
- scrollSpeed (number): Scroll speed (when scrolling occurs). 0 to 100. 100 is instant. Default is 100.
- scrollDelay (number): Time to wait after scrolling (when scrolling occurs). Default is 200.
- inViewportMargin (number): Margin (in px) to add around the element when ensuring it is in the viewport. Default is 0.####
scrollTo: (destination: PartialScrolls to the specified destination point.
- destination: An object with
and y coordinates representing the target position. For example, { x: 500, y: 300 }. Can also be "top" or "bottom".
- options (optional): Additional options for scrolling. Extends the options of the scroll function (below)####
scroll: (delta: PartialScrolls the page the distance set by
.- delta: An object with
x and y coordinates representing the distance to scroll from the current position.
- options (optional): Additional options for scrolling.
- scrollSpeed (number): Scroll speed. 0 to 100. 100 is instant. Default is 100.
- scrollDelay (number): Time to wait after scrolling. Default is 200.####
mouseDown / mouseUp: (options?: MouseButtonOptions) => PromiseMouse button up or down.
- options (optional): Additional options for mouse action.
-
Mouse button to click. Default is left.
- clickCount (number): Number of times to click the button. Default is 1.
#### getElement(selector: string | ElementHandle, options?: GetElementOptions) => PromiseGets the element via a selector. Can use an XPath.
- selector: CSS selector or ElementHandle to identify the target element.
- options (optional): Additional options.
-
Time to wait for the selector to appear in milliseconds. Default is to not wait for selector.####
getLocation(): VectorGet current location of the cursor.
$3
####
Installs a mouse helper on the page, making the pointer visible. Gets executed in the
initialization when passing visible=true. Use for debugging only.####
getRandomPagePoint(page: Page): PromiseGets a random point on the browser window.
####
Generates a set of points for mouse movement between two coordinates.
- start: Starting point of the movement.
- end: Ending point (or bounding box) of the movement.
- options (optional): Additional options for generating the path. Can also be a number which will set
.
- spreadOverride (number): Override the spread of the generated path.
- moveSpeed (number): Speed of mouse movement. Default is random.
- useTimestamps (boolean): Generate timestamps for each point based on the trapezoidal rule.How does it work
Bezier curves do almost all the work here. They let us create an infinite amount of curves between any 2 points we want
and they look quite human-like. (At least moreso than alternatives like perlin or simplex noise)
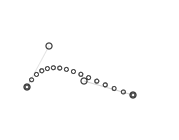
The magic comes from being able to set multiple points for the curve to go through. This is done by picking
2 coordinates randomly in a limited area above and under the curve.
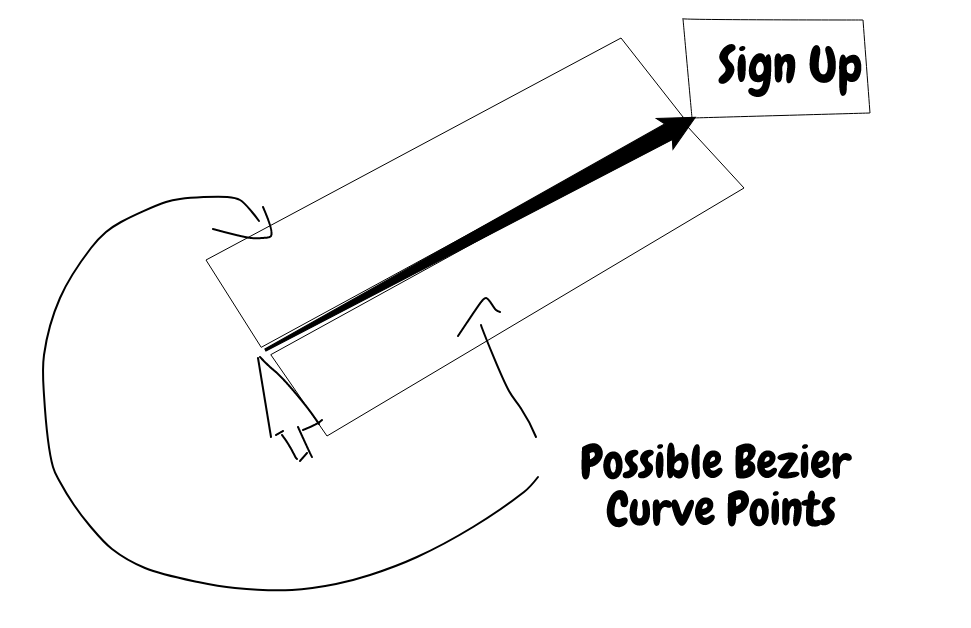
However, we don't want wonky looking cubic curves when using this method because nobody really moves their mouse
that way, so only one side of the line is picked when generating random points.
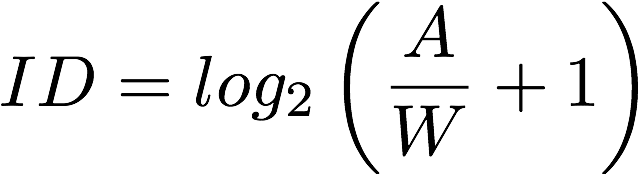
When calculating how fast the mouse should be moving we use Fitts's Law
to determine the amount of points we should be returning relative to the width of the element being clicked on and the distance
between the mouse and the object.
To turn on logging, please set your DEBUG env variable like so:
- OSX:
DEBUG="ghost-cursor:*"
- Linux:
- Windows CMD:
- Windows PowerShell: