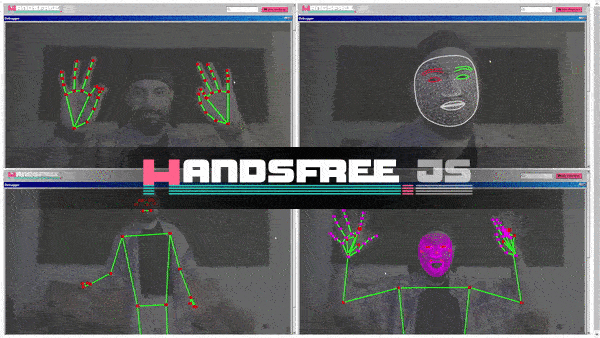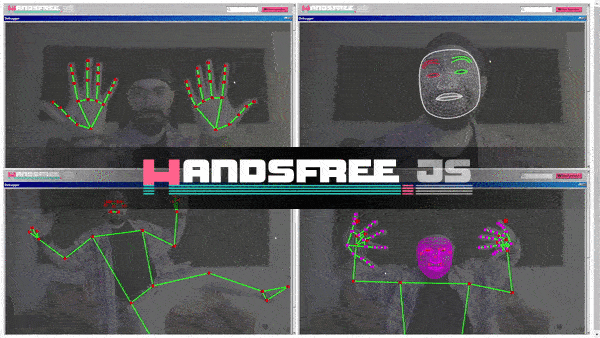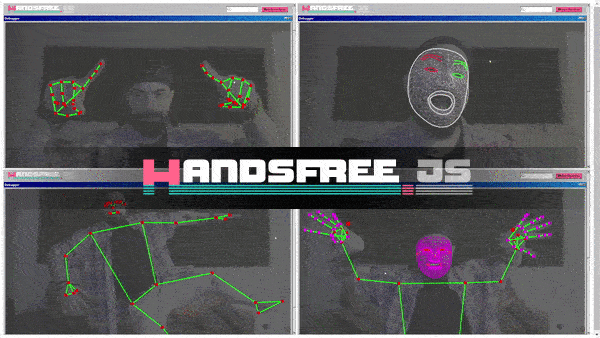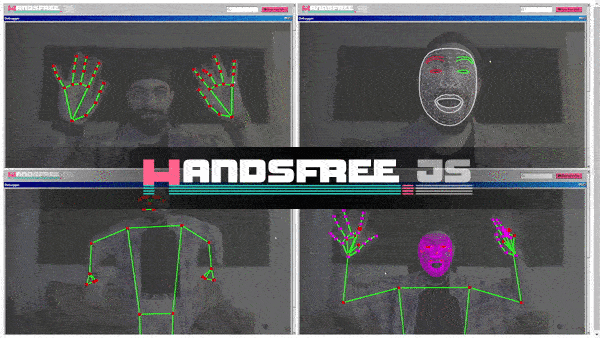
handsfree
v8.5.1
Quickly integrate face, hand, and/or pose tracking to your frontend projects in a snap ✨👌
0/weekUpdated 3 years agoApache-2.0Unpacked: 70.8 MB
Published by Oz Ramos
npm install handsfreeQuickly integrate face, hand, and/or pose tracking to your frontend projects in a snap ✨👌





Powered by:
💻 Project Documentation
I'm still experimenting with various ways to create documentation. The docs can be found:
- https://handsfree.js.org - This is the documentation that runs locally, and is the oldest docs
- https://handsfree.dev - This is the newer site hosted on WordPress, and includes the start of the Handsfree Plugin Repository
- https://codemedium.com/b1f09b783c034644acc1c873f347d6da - This is the Notion version of the documentation
Sorry for the confusion! I'll likely be settling on Notion but am still trying to find the best docs. Thanks!
Contents
This repo is broken into 3 main parts: The actual library itself found in
/src/, the documentation for it in /docs/, and the Handsfree Browser Extension in /extension/.
- Handsfree.js
- Quickstart with CDN (fastest way to get started)
- Quickstart with NPM (requires server or bundler)
- Development guide
- Handsfree Browser Extension
Quickstart
Installing from CDN
> Note: models loaded from the CDN may load slower on the initial page load, but should load much faster once cached by the browser.
This option is great if you don't have or need a server, or if you're prototyping on a site like CodePen. You can also just download this repo and work with one of the
/boilerplate/.
``
html
`
Installing from NPM
`bash
From your projects root
npm i handsfree
`
`js
// Inside your app
import Handsfree from 'handsfree'
// Let's use handtracking and enable the plugins tagged with "browser"
const handsfree = new Handsfree({showDebug: true, hands: true})
handsfree.enablePlugins('browser')
handsfree.start()
`
Hosting the models yourself
The above will load models, some over 10Mb, from the Unpkg CDN. If you'd rather host these yourself (for example, to use offline) then you can eject the models from the npm package into your project's public folder:
`bash
Move the models into your project's public directory
- change PUBLIC below to where you keep your project's assets
ON WINDOWS
xcopy /e node_modules\handsfree\build\lib PUBLIC
EVERYWHERE ELSE
cp -r node_modules/handsfree/build/lib/* PUBLIC
`
`js
import Handsfree from 'handsfree'
const handsfree = new Handsfree({
hands: true,
// Set this to your where you moved the models into
assetsPath: '/PUBLIC/assets',
})
handsfree.enablePlugins('browser')
handsfree.start()
`
Example Workflow
The following aims to give you a quick overview of how things work. The key takeaway is that everything is centered around hooks/plugins, which are basically named callbacks which are run on every frame and can be toggled on and off.
Quickstart Workflow
The following workflow demonstrates how to use all features of Handsfree.js. Check out the Guides and References to dive deeper, and feel free to post on the Google Groups or Discord if you get stuck!
`js
// Let's enable face tracking with the default Face Pointer
const handsfree = new Handsfree({weboji: true})
handsfree.enablePlugins('browser')
// Now let's start things up
handsfree.start()
// Let's create a plugin called "logger"
// - Plugins run on every frame and is how you "plug in" to the main loop
// - "this" context is the plugin itself. In this case, handsfree.plugin.logger
handsfree.use('logger', data => {
console.log(data.weboji.morphs, data.weboji.rotation, data.weboji.pointer, data, this)
})
// Let's switch to hand tracking now. To demonstrate that you can do this live,
// let's create a plugin that switches to hand tracking when both eyebrows go up
handsfree.use('handTrackingSwitcher', {weboji} => {
if (weboji.state.browsUp) {
// Disable this plugin
// Same as handsfree.plugin.handTrackingSwitcher.disable()
this.disable()
// Turn off face tracking and enable hand tracking
handsfree.update({
weboji: false,
hands: true
})
}
})
// You can enable and disable any combination of models and plugins
handsfree.update({
// Disable weboji which is currently running
weboji: false,
// Start the pose model
pose: true,
// This is also how you configure (or pre-configure) a bunch of plugins at once
plugin: {
fingerPointer: {enabled: false},
faceScroll: {
vertScroll: {
scrollSpeed: 0.01
}
}
}
})
// Disable all plugins
handsfree.disablePlugins()
// Enable only the plugins for making music (not actually implemented yet)
handsfree.enablePlugins('music')
// Overwrite our logger to display the original model APIs
handsfree.plugin.logger.onFrame = (data) => {
console.log(handsfree.model.pose?.api, handsfree.model.weboji?.api, handsfree.model.pose?.api)
}
`
Examples
Face Tracking Examples
Face Pointers

Motion Parallax Display

Puppeteering Industrial Robots

Playing desktop games with face clicks

Hand Tracking Examples
Hand Pointers

Use with Three.js

Playing desktop games with pinch clicks

Laser pointers but with your finger

---
Pose Estimation Examples
Flappy Pose - Flappy Bird but where you have to flap your arms

Local Development
If you'd like to contribute to the library or documentation then the following will get you going:
- Install NodeJS and git
- Clone this repository: git clone https://github.com/handsfreejs/handsfree
- Install dependencies by running npm i in a terminal from the project's root
- Start development on localhost:8080 by running npm start
- Hit CTRL+C from the terminal to close the server
Once you've run the above, you can just use npm start. If you pull the latest code, remember to run npm i to get any new dependencies (this shouldn't happen often).
Command line scripts
`bash
Start local development on localhost:8080
npm start
Builds the library, documentation, and extension
npm run build
Build only the library /dist/lib/
npm run build:lib
Build only the documentation at /dist/docs/
npm run build:docs
Build only the extension at /dist/extension
npm run build:extension
Publish library to NPM
npm login
npm publish
Deploy documentation to handsfree.js.org
deploy.sh
`
Dev Notes
- See vuepress-component-font-awesome for adding new icons to the documentation. Remember to run npm run fa:build when adding new font icons so that they are copied over into the docs/.vuepress/components/FA folder
- You may occasionally need to restart server when adding new files to the /docs, this is true when changing /docs/.vuepress.config.js as well
The Handsfree Browser Extension
The Browser Extension is a designed to help you browse the web handsfree through face and/or hand gestures. The goal is to develop a "Userscript Manager" like Tampermonkey, but for handsfree-ifying web pages, games, apps, WebXR and really any other type of content found the web.
How it works

- When you first install the extension, /src/background/handsfree.js checks if you've approved the webcam. If not, then it'll open the options page in src/options/stream-capture.html
- The popup panel has a "Start/Stop Webcam" button that communicates with the background script to start the webcam: /src/popup/index.html
- The background page is where the models are stored and run. This keeps everything isolated and only asks for webcam permission once (vs on every domain): /src/background/handsfree.js
- The background page also uses the "Picture in Picture" API to "pop the webcam" out of the browser. It renders the webcam feed and debug canvases into a single canvas, and uses that as the srcObject to a separate video element which is the PiP'ed
How to install
$3
Install as an unpacked chrome extension.
1. Visit chrome://extensions`
2. Enable Developer Mode on the top right
3. Then click Load unpacked and select this project's root folder

Handsfree Browsing
By default, each page will get a "Face Pointer" or a set of "Palm Pointers" for you to browse pages handsfree.
!A person controlling a virtual mouse pointer by tilting their head around
!A person scrolling a page by pinching their index and thumb together and raising or lowering their pinched hand
However, in addition to the pointers you can add custom handsfree interactions. For example, here's a demonstration of handsfree-ifying different things:
!Creating generative art with hand gestures
!A person pinching the air to "pinch" a blob. Moving a pinched blob causes it to sing in a different pitch
Explore the interactive docs at: Handsfree.js.org
Or try it right away with the serverless boilerplates in /boilerplate/!
License & Attributions
License: Apache 2.0
The Handsfree.js core is available for free and commercial use under Apache 2.0. Each of the models are also available for free and commercial use under Apache 2.0:
- Jeeliz Weboji (Apache 2.0)
- MediaPipe Models (Apache 2.0)
- TensorFlow.js Models (Apache 2.0)
Attributions
I'd like to also thank the following people and projects:
- 98.css by @jdan (MIT) - Used as boilerplate for documentation theme
- [handpose-facemesh-demos by [@LingDong-]](https://github.com/LingDong-/handpose-facemesh-demos) - Used as a boilerplate for the Handpose Three.js setup
---
Special Thanks
- @Golan and the The STUDIO for Creative Inquiry for hosting me for a residency during 2019 and for helping me approach projects in a more expressive way. Also for inviting me back for a multi-month residency in Spring 2021!
- @AnilDash for supporting the project during Winter 2018 out of the blue and the opportunities to share my project on Glitch.com
- The School of AI for the 2018 Fellowship in support of this project
- @jessscon and Google PAIR for the very early support that made starting this project possible
- Everyone who's previously supported the project through GitHub Sponsors, Patreon, GoFundMe, and through Twitter and everywhere else over the years