High Prefomance Monadic Reactive State Container for React
npm install react-most``
(>'o')> ♥ <('o'<)
_ _ _ _ |_ _ _ _ |_
| (- (_| (_ |_ ||| (_) _) |_

A Monadic Reactive Composable State Wrapper for React Components





npm install react-most --save
What
is a simple, 100 LOC Higher Order Component for React. Its only dependencies are most, most-subject.Data flow in
react-most is simple and unidirectional, similar to flux.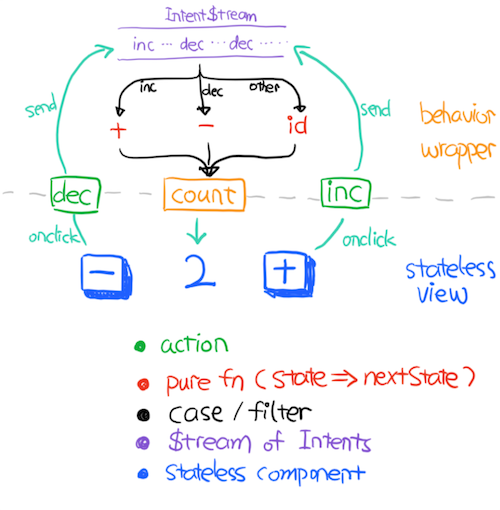
Terminology
- Machine: a machine can emit Update to a timeline update$, and can be operated by calling function in actions
- Plan: a Plan is a function that describe how to create a
- Update: a function
- Action: a function that create Intent
- Intent: describe what you want to do
- Intent Stream: a timeline of every created by every ActionQuick Start
sorry we don't have a book to document how to use , and I don't really need to, but
there's only 3 things you should notice when using react-most, I'll explain by a simple counter app.Also, you can refer to:
- various Examples
- simple API
- Best Practices
- Wiki
$3
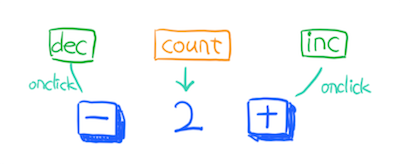
`html
const CounterView = props => (
{props.count}
)
`
$3
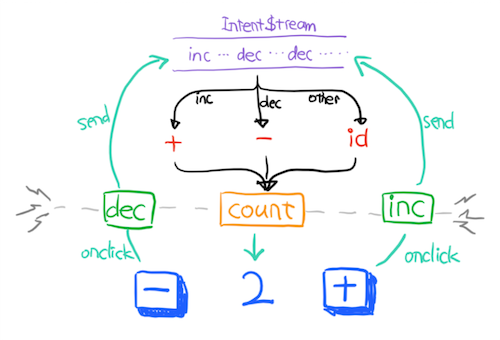
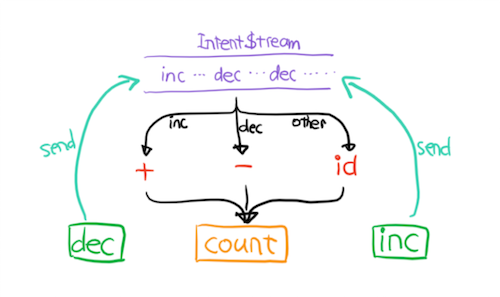1. A counter can have actions of
and dec, which will send Intent of {type: 'inc'} or {type:'dec'} to Intent Stream upon being called.
2. A counter reactively generates Update when it receives an Intent of either type inc or dec.`js
const counterable = connect((intent$) => {
return {
update$: intent$.map(intent => {
switch (intent.type) {
case 'inc':
return state => ({ count: state.count + 1 });
case 'dec':
return state => ({ count: state.count - 1 });
default:
return _ => _;
}
}),
actions: {
inc: () => ({ type: 'inc' }),
dec: () => ({ type: 'dec' })
}
}
})
`
you'll see that the function in parameter is a Plan, the object it return is a Machineand
return a HoC that you can wrap it to View Component$3
`js
const Counter = counterable(CounterView)render(
document.getElementById('app')
);
`Features
Inspired by Redux and Functional Reactive Programming, allows you to model user events, actions, and data as reactive streams. Now you can map, filter, compose, and join those streams to form your application's state.$3
In imperatively written code, you describe step-by-step how to process data. With react-most, we simply define data transformations, then compose them to form our data flow. There are no variables, no intermediate state, and no side effects in your data flow's data composition!$3
In Redux, reducers' use of switch statements can make them difficult to compose. Unlike reducers, sinks are reusable observable object.Wrapper is simply a function and easily composable.
`js
const countBy1 = connect(...)
const countBy2 = connect(...)
const Counter = countBy1(countBy2(CounterView))
// or
const counterable = compose(countBy1, countBy2)
const Counter = counterable(CounterView)
`$3
Because UI and UI behavior are loosely coupled, you can test a React component by just passing it data. Behaviors can be tested by calling actions and then verifying the state.js
import {stateHistoryOf, Engine } from 'react-most-spec';
let counterWrapper = TestUtils.renderIntoDocument(
)
let counter = TestUtils.findRenderedComponentWithType(counterWrapper, Counter)
counter.actions.inc()
counter.actions.inc()
counter.actions.inc()
expect(stateHistoryOf(counter)[2].count).toBe(3)
`see more details about testing at react-most-spec or todomvc example
$3
Asynchronous functions, such as Promises, can be converted to a stream and then flat-mapped.js
intent$.map(promise => most.fromPromise(promise))
.flatMap(value => / use the results /)
`$3
Transducer is another high-performance, functional way to compose non-monadic data flows.Writing actions as transducers can improve reusability.
$3
Because we have all actions' streams, we can easily reproduce the actions at anytime, or get snapshot of the state's stream and going back in time.By passing the
parameter into the options of connect
js
connect(intent$=>[/ your awesome flow /], { history: true })(App)
`or passing
as a prop
`js
`A stream with all of the state's history will be created, called
.$3
If you're more familiar with RxJS, it's easy to use it with react-most in place of most. Simply pass a prop called engine to the Most component.> But, I'm strongly RECOMMEND to use the default engine
most.js, it's how react-most originally built for, and production ready.`html
import rxEngine from 'react-most/engine/rx'
``